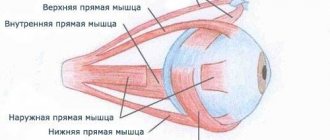
What is a conjunctival dermoid cyst?
A cyst is a formation on the conjunctiva. It is not filled with anything and can disappear on its own. Often noticeable only in the morning. In general, cysts are usually called dermoid (benign). In appearance it resembles a bubble.
Types: retention, dermoid
Types of conjunctival cyst:
- teratoma (hard, retention, can degenerate into malignant);
- exudative (traumatic);
- pigment (medicinal);
- congenital (developmental anomaly, has a greater predisposition to growth).
The typology of the cyst can only be determined by a specialist.
If you detect any strange formation on the conjunctiva, you should consult an ophthalmologist. You should not touch your eyes with your hands, rub or try to remove a possible cyst yourself.
A product for moisturizing and protecting the sclera - instructions for Iridina eye drops.
Cysts can often go away on their own without medical intervention.
What kind of disease is iridocyclitis read in the article.
What kind of disease is this - conjunctival cyst, code according to ICD-10
The conjunctiva is the mucous surface of the eyeball. It performs a protective and moisturizing function, protecting the eye from external influences. Past infectious diseases, injuries, and even structural features of this membrane can cause problems.
In addition, the appearance of a neoplasm can be promoted by long-term use of eye drops with a strong effect or the presence of parasites in the organ. In some cases, the cause of this pathology cannot be determined.
This material will help you understand what subconjunctival hemorrhage of the eye is and what it looks like.
Here's a video of what the disease looks like:
In the ICD disease classifier - 10, conjunctival cysts are defined by the following codes:
- D 31.0 - benign neoplasm of the eye and its adnexa.
- C 69.0 - malignant neoplasm of the eye and its adnexa.
- H 33.1 - parasitic, pseudocyst.
- H 11.4 - other conjunctival vascular diseases and cysts.
Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis, so if any foreign inclusion is detected on the outer shell of the eyes, you need to see an ophthalmologist.
Causes
A conjunctival cyst can occur due to:
- fibrosis after conjunctivitis;
- eye injuries;
- surgical intervention;
- scleritis;
- genetic factors.
The tumor may appear for no apparent reason or from simple rubbing of the eye.
Determining the cause of the cyst is important to determine its type and prescribe further therapy.
Smart correction - which glasses lenses are best to choose.
Tonometry
Find out when the prescription of Catarax eye drops is indicated here.
Causes
Congenital conjunctival cysts are genetically determined diseases of the organ of vision. Dermoid is a teratoma that occurs alone or in combination with other manifestations of Goldenhar syndrome (anomalies in the structure of the ears, lower jaw, tongue, palate and teeth), Madelung deformity or branchial arch syndrome. The cause of the development of a dermoid cyst is a violation of the differentiation of the germ layers that give rise to the structures of the eyeball. In most cases, conjunctival cysts are a consequence of post-inflammatory fibrosis, which occurs in patients with conjunctivitis of bacterial, viral or fungal origin, scleritis, canaliculitis, or, less commonly, a history of blepharitis. An etiological connection is traced between this pathology and acquired dilatation of the excretory ducts of the accessory lacrimal glands. Intraepithelial cysts often form after injury to the eyes, prolonged friction of the eyelashes during inversion or eversion of the eyelids. Subepithelial cysts can result from surgery. The reasons for the development of retention cystic formations are obstruction of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands of Krause and Wolfring, and impaired lymphatic drainage. Acquired forms can develop after surgical treatment of strabismus or removal of the eyeball by evisceration with resection of the posterior pole and preservation of the cornea. The trigger for early complications after surgical treatment of strabismus is often poor-quality suture placement on the conjunctiva, leading to disruption of the location of Tenon’s capsule. In the late postoperative period, the cause of cyst formation is the penetration of cells from Tenon's capsule in the area of the scleral tunnel incision. Cystic formations after evisceration develop in the area of the musculoskeletal stump (MS). The etiological factor is the increased proliferation of cells of the conjunctiva of the limbal zone. If the congruence of the contacting surfaces of the prosthesis and the ODC is disturbed, the pressure in the orbital cavity changes sharply. Varying degrees of pressure on adjacent tissues and their prolonged injury lead to the formation of a callus-type cyst.
Symptoms and diagnosis
You can suspect the presence of a cyst based on the following signs:
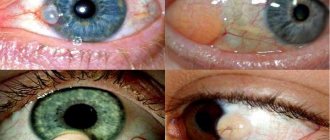
- visual presence of yellow or brown spots on the white of the eye;
- tearfulness;
- pain in the eyes;
- discomfort;
- redness of the white;
- movement of the eyeball may occur;
- sometimes there is a cloudy spot in visual perception.
Sometimes the cyst does not manifest itself in any way other than being visible on the sclera. Even if other symptoms are not felt, you should consult a specialist.
When an invisible enemy creates noticeable problems - eye demodicosis symptoms and treatment.
Tearfulness is one of the first signs of cyst development
Diagnosing education is not difficult. This is done by using:
- visual inspection;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- histology and biopsy of the material (after removal).
Tissue examination after separation of the cyst is necessary to determine the atypicality of the formation.
How to treat retinal dystrophy is described in detail in the article.
Retention view
Before starting treatment, carefully read the instructions - instructions for using Katachrom eye drops.
Why is a lacrimal caruncle cyst dangerous?
The main task of the lacrimal apparatus is to protect the eyes from environmental influences and protect the cornea and conjunctiva in order to maintain normal humidity levels.
A cyst in the area of the lacrimal caruncle is formed extremely rarely and only in those people whose lacrimal canaliculi are covered with thin hairs. This organ is not a working one in the human body.
Fortunately, atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle does not become malignant and does not affect vision . But still, a person experiences the following unpleasant symptoms:
- burning sensation in the eye;
- it feels like there is a foreign body in the area of the lacrimal caruncle;
- dry eye;
- pain is usually absent;
- The lacrimal caruncle may become enlarged and reddened.
For what reason atheroma forms in this part of the eye, scientists will not say with certainty, but the following circumstances can presumably influence it:
- when fallen eyelashes penetrate the eye;
- foreign objects entering the eye;
- microtrauma of the eye and penetration of infection through it.
The following changes in the eye are complications of atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle:
- suppuration;
- inflammation;
- infectious damage to other structures of the organ of vision.
Doctors recommend not to wait for complications and to remove such wen; the operation is performed under local anesthesia; children under 7 years of age receive general anesthesia.
Important! If the purulent contents of the atheroma penetrate the skin, it will enter the bloodstream, and this is fraught with blood poisoning, which most often leads to the death of a person.
Treatment methods for dermoid on the eye
The choice of dermoid treatment method depends on:
- localization of education;
- quantities;
- extent of distribution;
- reasons for occurrence.
Medication
Conservative treatment includes:
- eye drops;
- antibiotics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- trichloroacetylic acid injections.
The following are prescribed as eye drops:
- moisturizing (Defislez, Alkon Systane, Slezin);
- anti-inflammatory (Dexamethasone, Inndocollir, Tobradex).
During treatment of a conjunctival cyst, it is forbidden to use contact lenses to avoid additional infection.
To prevent dry eye syndrome from interfering with your life and work, use Cationorm eye drops.
Differential diagnosis
Operations
If there is no effect from conservative methods, the patient may be indicated for surgery:
- surgical;
- laser
Surgical intervention:
- carried out in the presence of a voluminous education;
- Before surgery, local anesthesia and contrast agent are administered;
- the painted area is removed and a self-absorbing suture is applied;
- In some cases, plastic surgery is performed.
Laser Application:
- necessary for small-sized formations;
- the affected area is cauterized with a special beam.
Artificial tears will help relieve discomfort
Advantages of laser surgery:
- short rehabilitation period;
- absence of cosmetic defect;
- bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect;
- there is no chance of infection;
- passes almost always without complications.
This method is not used for large lesions due to the risk of burning the conjunctiva. The contents heat up and the cyst may rupture.
After any intervention, the patient is prescribed a gentle regime and anti-inflammatory therapy. Forbidden:
- lift weights;
- visit the pool and sauna;
- use cosmetics;
- wear contact lenses.
In some cases, treatment of the cyst is not indicated for the patient. Regular outpatient monitoring and specialist supervision are carried out. Even after removal, the risk of pathology returning remains.
The tumor may fester. Inspections should be performed as often as possible.
Read what the diagnostic method of keratometry is here.
Non-steroidal pain reliever
Treatment
Cysts can be treated in several ways. Applicable:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- laser
The doctor must choose the right method after examining and examining the patient.
Conservative treatment consists of disinfecting the damaged root, cleaning the tooth and treating it. Sometimes a special suspension is introduced, which contains calcium and copper. Next, a small current discharge is applied to the tooth.
The therapeutic method is used if:
- filling on the root canals ;
- small size of cystic formation;
- There is low-quality filling.
What symptoms can be used to recognize osteogenic sarcoma of the jaw?
They are treated with a special drug that has a detrimental effect on the contents of the capsule. After this, all pus is removed, and the cleaned cavity is filled with dental paste, which restores the bone structure. At the end of the entire process, the doctor fills the tooth. After such therapy, relapses are possible.
The dentist decides to combat the problem surgically in advanced cases. This happens in 85%.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- pin in the tooth canal;
- installed prosthesis on a diseased tooth;
- the size of the formation is more than 9 mm;
- pain and swelling of the gums.
There are several methods of surgical treatment in modern medicine:
- Cystotomy . The anterior wall of the tumor is removed. Such intervention is indicated for large cysts, if the bony floor of the nose or the palatal plate is severely damaged. The postoperative period is long and painful.
- Cystectomy . This is a complex but effective operation. The entire cavity, shells and partially roots are removed. It is carried out when the cyst grows rapidly in the upper jaw area.
- Hemisection . The cyst is removed, the entire root or partially, the entire tooth or part of it.
After any operation, you should prepare for a long recovery period. You need to rinse all the time in order to disinfect the wound.
In some cases, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Aspirin is contraindicated because it causes bleeding. In some cases, a particularly difficult period lasts only a day. Swelling and pain disappear within a week.
Laser treatment is an equally effective and popular method. The laser beam removes the cyst painlessly, there is no risk of infection. Recovery after this manipulation is very fast.
The whole process happens as follows:
- are opened and expanded .
- is introduced into the prepared area .
- The process of tumor removal and disinfection takes place.
- The opening and expansion of the dental canals takes place
All about laser removal of dental cysts
The method is good, but expensive, not everyone can afford such treatment.
Remember! Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
What is the danger of the disease
The appearance of a conjunctival cyst in itself is not dangerous. Neglected forms may result in:
- tumor growth;
- visual impairment;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- degeneration of pathology into a malignant form.
Any non-standard formation on the sclera of the eye must be shown to a specialist.
If there is a need or a bad family history, it is better to remove the cyst immediately to avoid consequences.
An examination will help you quickly and correctly establish a diagnosis.
A dangerous disease that cannot be left untreated is keratopathy.
Prevention of occurrence
The reasons for the appearance of atheroma on the eyelid are blockage of the sebaceous glands, lack of personal hygiene or a weakened immune system. There are no specific measures to prevent the disease. All rules are general in nature, but, nevertheless, are effective.
If a person follows the following recommendations , then even with a hereditary predisposition, he will be able to avoid the appearance of atheroma on the eyelid:
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules, for example, taking regular showers.
- Remove makeup with high-quality cosmetics.
- Nutrition should be balanced and include more plant foods.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- If a person is forced to work in hazardous work, he should wear special protective clothing and face masks.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner. Do not let the process become chronic. This is especially true for diseases associated with the ears, nose and oral cavity (for example, carious teeth).
- Also try to eliminate endocrine disorders in a timely manner.
- Monitor the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, eliminate diarrhea and constipation in a timely manner.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for detecting a conjunctival cyst is favorable. If you consult an ophthalmologist in time, you can avoid any consequences. Preventive measures include:
- compliance with hygiene standards and rules (removing makeup, prohibiting rubbing eyes with hands, etc.);
- timely examinations by a specialist;
- regular replacement of contact lenses when using this method of vision correction;
- self-massage.
We also recommend that you read our article which will tell you how to put on lenses for the first time.
If the disease is manifested in relatives, the patient must consult an ophthalmologist at least 2 times a year.
After surgery it is not recommended to swim in the pool
Prevention of development
Preventive measures will include:
- visual hygiene: wearing clean contact lenses, replacing them in a timely manner, carefully removing makeup;
- preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist;
- exclusion of aggressive factors: chemical influences and various types of radiation, including ultraviolet.
When working with harmful production factors, it is mandatory to use personal protective equipment.
Cysts, although benign formations, can cause many unpleasant consequences, including loss of vision. Timely treatment and removal of formations is a measure that will allow this to be avoided. And in the conditions of modern equipment of medical clinics, ophthalmological care is provided quickly and efficiently.
Feedback on treatment results
Reviews from patients indicate that the choice of treatment method for conjunctival cysts is purely individual. Surgical intervention or drug treatment is based on determining the size of the formation and the degree of spread.
- Marina, 34 years old, Olenegorsk: “I treated a conjunctival cyst twice. The first time - with the help of drops. It resolved quite quickly. It’s just not clear: spontaneously or due to the effects of the drug. Now I had to have surgery because the pathology had returned. It went by very quickly. There’s nothing left anymore.”
- Vladimir, 40 years old, Nizhny Novgorod: “The cyst appeared not so long ago. It grew very quickly. It became difficult and painful to watch. The doctor decided to perform surgery. After it, the eye began to look terrible. I had to resort to plastic surgery. Everything is fine now, I hope there will be no relapse.”
- Svetlana, 58 years old, Saransk: “My grandson has a small lesion on the white of his eye. They showed him to the ophthalmologist. It turned out that it was a cyst. The doctor recommended not to use anything for now. And he turned out to be right. The cyst resolved on its own in just a couple of weeks.”
See the world with healthy eyes
Neoplasms of the eye
On the eyelid, atheromas are not large, reaching a diameter of 5-10 mm, but sometimes they can be the size of a walnut (up to 2 cm). If the formation is small, then it does not cause inconvenience to a person, but a large atheroma, and even in a visible place, brings many problems to its owner.
But not only in aesthetic terms, a wen can cause harm. If it has grown to an impressive size, then such a formation begins to compress neighboring tissues, blood vessels and nerve endings, causing headaches and dysfunction of those systems and organs that the atheroma has compressed. The person may also feel soreness in this area.
When removing atheroma on the eyelid, the doctor must refer the patient to a consultation with an ophthalmologist .
Diagnostics
Dermoid cysts are detected by the following methods:
- Visually during the initial clinical examination.
- Using ultrasound (most relevant for localization in the ovary).
- Using magnetic resonance imaging (a similar examination is used if there is a suspicion of a brain cyst).
Sometimes tests are taken for tumor markers, among which the most significant are CA 125 and HE 4, but still they are of secondary importance compared to the rest of the diagnosis.
Often the results of these tests are false positive. For example, due to a chronic source of inflammation in the body.
Which doctor will help?
To receive qualified medical care, be sure to consult your doctor.
The disease described here requires the participation of several specialists (depending on the location of the cyst and the degree of its danger in terms of degeneration):
- surgeon (general, pediatric, maxillofacial, proctologist, neurosurgeon) - the main basic specialist for this problem;
- neurologist - relevant if pathology is detected in the brain;
- ophthalmologist - cyst in the area of the eyeball;
- gynecologist - ovarian cyst;
- oncologist - this specialist monitors for malignancy;
- therapist - general supervision.
The timing of the medical examination is of great importance. If the cyst is immature, it can be very small. And it can be missed even with an ultrasound. Especially if the ultrasound is not aimed at finding a cyst.
Necessary tests
Blood samples
Among blood tests, only tests for tumor markers make sense.
In addition to those already mentioned above, they can carry out extended, additional:
- CA 19-9;
- REA;
- M-CSF.
A general blood test is rarely done, but it can show the presence of inflammation in the body and the general status of the body.
A detailed description of the ultrasound examination of teratoma is important:
- exact location;
- exact dimensions;
- presence of cavities and liquid;
- solid contents;
- capsule structure.
Identifying the size and nature of the tumor (mature or immature) will help determine the urgency of treatment.
It is better not to touch a very small cyst without signs of any dynamics.
There is ultrasound navigation, under which laparoscopic examination is performed.
Laparoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic surgical procedure in which a laparoscope (a telescopic device, which is a flexible lens system with digital video transmission capability) is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision (on average 1 cm).
A small amount of carbon dioxide is also pumped in to create an operational space.
Microsurgical instruments are used to perform surgery and collect biomaterial for histological examination.
Possible complications
Obviously, internal dermoids that directly touch the internal organs pose a greater danger.
Main complications:
- Cyst rupture. — Violation of the integrity of the neoplasm, often accompanied by heavy internal bleeding. — Usually happens during extreme physical exertion or mechanical trauma (for example, a blow to the cyst area). — A sure sign: persistent, gradually increasing local pain of a “spill over” nature.
- Inflammation and suppuration of pathological formation. — Often occurs against the background of an exacerbation of some chronic infection, when the pathogen penetrates the cystic tissue. — Here the main symptom is not pain, but a sharp increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, nausea, vomiting, general weakness, and generally signs of sepsis.
- Torsion of the legs. — The dermoid cyst has a pedicle attachment, which can twist spontaneously or from mechanical trauma. — A characteristic, shooting pain occurs, which radiates to neighboring organs. - Body temperature also rises. Attacks of severe weakness occur.
Emergency care here is only surgical. The person must be urgently taken to the nearest clinic for surgery.
When a purulent process occurs, subsequent antibiotic therapy is required. Sometimes, after removal of the dermoid, false cysts may reappear in the same place.