Structural features
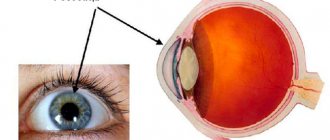
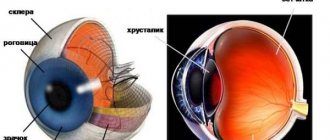
The cornea is the outermost layer of the eyeball, a transparent, avascular, mirror-like sphere. It has tiny dimensions (diameter - 0.56 mm) and occupies 1/16 of the outer surface of the eye. Consists of several layers separated by membranes.
The main guard is the outer epithelium. Prevents the penetration of dangerous microorganisms into the eye, delivers oxygen from the tear film, and controls the flow of fluid. It will hurt if you accidentally touch the epithelium with your hands. It contains nerve endings.
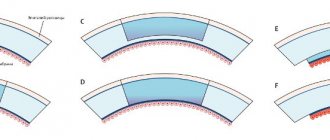
The second guard is the dense anterior membrane. In addition to protection, it nourishes the cornea. Thickness – 8-10 microns. Next comes the central part of the shell - an elastic and strong collagen stroma. Its cells repair damage. Then again there is an intermediate layer (Descemet's membrane). The last layer, the endothelium, prevents the cornea from swelling and maintains transparency.
| At a young age, it contains about 4 thousand cells. By old age, only 2.5 thousand have the ability to regenerate. |
Treatment of keratoconus
Treatment of keratoconus of the eye with medications, unfortunately, is not yet possible. Taufon and other similar drugs are intended to nourish the eye tissue and relieve burning and dryness in the visual organs. Therefore, such medications can only be part of complex therapy when choosing a specific treatment method.
In the initial stages of keratoconus, conservative treatment methods are used. More severe forms of keratoconus require surgery. Traditional medicine is also used.
Vision correction with glasses is prescribed first. While their use brings a therapeutic effect, the use of contact lenses is not allowed. The reason is quite clear: lenses can cause microtrauma to the surface of the eye.
Only when the situation with the conicity of the cornea changes the refraction of the image does the selection of glasses stop. This optical device is being replaced by lenses, the selection of which occurs individually, taking into account the stage of the disease and the capabilities of the body:
- Soft lenses do not scratch the cornea, but their use can correct vision only when it protrudes slightly. Practice shows that such lenses are not very suitable for keratoconus: taking the shape of the cornea, they do not create a tear film, which is why the refractive power of the eye does not improve;
- Hard lenses are made individually and therefore have a great therapeutic effect. While maintaining their shape, they are able to eliminate curvature of the cornea. A tear film can already form between these lenses and the eye. The disadvantage of lenses is that they create discomfort when worn on a damaged cornea;
- Hybrid lenses consist of a hard center and a soft rim, combining benefit and comfort. Recommended for those who find wearing hard lenses very inconvenient.
The development of medicine has made it possible to develop several options for surgical correction, but only a doctor should make the choice in favor of a specific operation. The most modern method is the introduction of colorless rings into the corneal tissue (implantation of intrastromal rings), which will bring its shape closer to its natural one. However, the operation is not able to stop the course of the disease.{banner_gorizontalnyy2}
Corneal crosslinking surgery is a modern and safe treatment method and has a short rehabilitation period.
Also popular is keratoplasty, an operation in which donor tissue is placed in place of damaged tissue. It is recommended for severe deformation of the cornea as a result of other treatment methods, but carries the risk of dangerous complications such as glaucoma and rejection of the transplanted tissue. Finally, in the most advanced cases, a corneal transplant is used. This operation is the only way to stop the course of the disease. The most qualified clinic for the treatment of keratoconus is the Fedorov Clinic in Moscow.
Traditional methods should be resorted to in the early stages of the disease in order to slow down the progression of the pathology. You can use traditional medicine during the rehabilitation period, but you need to understand that it is impossible to straighten the cornea using these methods. But compresses prepared with chamomile flowers help relieve eye itching and relieve excessive tension from the sore spot.
Abnormalities of corneal development that do not require treatment
If the radius of curvature, size, and transparency of the shell do not meet medical standards, then they speak of a developmental anomaly.
| The eyes are not only a mirror of the soul, but also of a person’s physical health. |
Poor nutrition throughout life does not go in vain and comes back to haunt you in old age. Violation of fat metabolism and cholesterol after 80 years leads to the accumulation of lipids in the cornea, its clouding in the shape of a ring. This anomaly is called a senile arc. The disease does not affect vision, and therefore cannot be treated in any way.
With dysfunction of the nervous system and liver, copper metabolism is impaired. A brown-green hoop appears around the cornea - the Kaiser-Fleischner ring. It does not affect vision.
Developmental anomalies subject to correction
A large cornea or megalocornea is found in babies at birth. The norm is considered to be a shell diameter of 10 mm. If it exceeds by at least 1 mm, then this is a corneal symptom. The refraction of the eye is impaired - the larger the radius of curvature of the lens, the lower the refractive power.
The defect is dangerous for a number of complications - glaucoma, cataracts, problems with the retina. Megalocornea is often a symptom of complex genetic diseases (Markesani syndrome, Marfan syndrome, etc.). The disease has no cure. To improve vision, corrective glasses and lenses are prescribed.
Microcornea or small cornea. The opposite case. The shell, on the contrary, is less than 10 mm in diameter. The pupil appears unnaturally small. The consequence of microcornea is farsightedness. Glaucoma, cataracts, etc. develop against the background of the disease. If the cornea remains transparent, the doctor will prescribe symptomatic treatment and telescopic devices for vision correction.
Return to contents
| Both cases (macro-, microcornea) are of genetic origin and are inherited. |
Symptoms
Manifestations of corneal inflammation will be as follows:
- dry eye syndrome, pain, pain;
- tearfulness;
- heavy eyelids - eyes seem difficult to open;
- fear of light;
- twitching of eyelids;
- headache;
- redness;
- decreased vision.
| These symptoms are nonspecific and are often associated with other eye problems. Be that as it may, such manifestations should be alarming, and it is better to be aware of them. |
During the examination, the ophthalmologist will record:
- internal swelling;
- decreased sensitivity;
- cloudiness;
- dilated vessels;
- sores on the shell.
Symptoms of keratoconus
Initially, symptoms of keratoconus are similar to other eye diseases. A person complains of severe eye fatigue, double images when looking at light objects on a dark background, the appearance of spots before the eyes, and the presence of discomfort. If the process of development of pathology begins to progress rapidly, visual acuity will decrease, as happens with myopia or astigmatism. In the early stages, wearing glasses or contact lenses helps overcome visual impairment; later, optical correction loses its effectiveness.
Vision in keratoconus decreases gradually. Due to the increase in the number of diopters, the patient has to change glasses frequently. However, this cannot always guarantee a positive result. Pathology can sometimes progress so quickly that changing glasses does not have time to adjust vision. Contact lenses may also not be helpful due to the abnormal convexity of the cornea. In this case, the patient should begin serious treatment of the visual organs.
Typically, the stages of development of keratoconus continue for 10–15 years, sometimes this is delayed for a longer period of remission. Only in 5% of cases does the disease suddenly develop into an acute form, in which Descemet’s membrane ruptures and intraocular fluid leaks out.
Diseases of the cornea of the eye
Keratitis
This disease is characterized by clouding of the membrane and decreased vision due to viruses and bacteria. Inflammation can be caused by:
- herpes simplex and herpes zoster, chickenpox, measles, adenovirus;
- bacteria - intestinal, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus, diplococcus.
- pathogens of tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, etc. (cause purulent keratitis);
- various fungi.
| Those who use contact lenses incorrectly should be wary of amoebic infection, the culprit of severe keratitis. |
Secondary causes of the disease:
- Drying of the cornea;
- Exposure to too much light, such as when welding.
- Foreign body injury.
- Allergy.
- Diabetes.
- Mechanical damage to the cornea during eye surgery.
The most unfavorable outcome is epithelial detachment and the formation of corneal ulcers. Tissue necrosis occurs, purulent wounds appear, causing severe pain and a sharp change in vision.
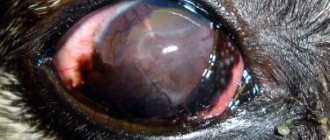
Keratoconus
Doctors make this diagnosis if the cornea is not round in shape, but in the form of a cone. The pathology develops over 20 years. During adolescence, an ophthalmologist may mistakenly detect astigmatism.
Signs of keratoconus:
- When one eye is closed, double vision occurs.
- A person sees poorly from any distance.
- Blurred vision at night.
- Optical illusion. The patient observes not one, but several images at once.
- Oversensitive, intense eyes.
Return to contents
Keratomalacia
This disease often affects newborns whose mothers did not receive enough vitamin A during pregnancy. Or children who have suffered from jaundice. The disease develops rapidly. You can be left without vision in a day.
Bullous keratopathy
Bullae are blisters that cover the cornea. They occur after eye surgery, lens implantation, secondary glaucoma, resulting in the death of endothelial cells. Passed on by inheritance.
Corneal dystrophy
Or a tissue nutritional disorder. This condition is caused by disruptions in the functioning of the immune system, injuries, infections, and hereditary factors. Dystrophies are divided into:
- stromal;
- epithelial;
- endothelial;
- membrane
Iridocyclitis
Deep infectious inflammation of the vessels of the cornea. The eye becomes completely red from blood impurities. Young people and middle-aged people get sick.
Xerophthalmia
In other words, dry eyes. An urgent problem for our time.
Causes:
- With the advent of new means of entertainment - televisions, computers, telephones, our eyes began to experience double stress.
- Inaccurate use of lenses, failure to comply with an adequate wearing regimen.
- Poor environment, dusty air.
- Avitaminosis.
- Chronic diseases of the conjunctiva.
- Trachoma, diabetes, thyroid problems.
In advanced cases, the mucous glands may simply die and the conjunctiva may disintegrate.
Corneal damage
The eye shield is easily injured. They poked a finger into an eye unsuccessfully, scratched it with a fingernail, touched it with a branch, got hit by a speck, etc. Types of damage:
- burns;
- foreign bodies;
- wounds;
- erosion.
Diagnosis of corneal diseases
The doctor conducts a detailed survey of the patient and assesses the condition of the eyes using traditional means:
- slit lamp;
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- perforated diaphragm;
- fluorescein staining;
- biomicroscopy;
- pachymetry;
- confocal microscopy;
- keratotopography;
- culture for bacteria.
Ophthalmology has come a long way. The latest equipment allows us to qualitatively identify defects at an early stage. For example, many clinics use laser photo recorders, optical tomographs, and endothelial microscopes.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of keratoconus
The beginning of detection of ocular keratoconus is the moment the patient contacts an ophthalmologist with a complaint of deteriorating vision. After the interview, the doctor measures visual acuity and eye refraction. If the presence of myopia or farsightedness is not confirmed, the examination of the patient will continue. The following diagnostic methods exist:
- Skiascopy. Using a special device (skiascope), the counter-movement of shadows specific to keratoconus, called the “scissors effect”, is determined;
- Keratometry is the most common diagnostic method in which the curvature of the cornea is determined;
- Refractometry. Using the technique, irregular astigmatism and myopia resulting from corneal deformations are detected;
- Computed tomography of the eye or ultrasound. These studies reveal changes in the tissues of the cornea, including scars on its surface.
In the later stages of the disease, its diagnosis is not difficult, since the pathology of the cornea is immediately visible without special devices. Only examinations are required to determine the extent of damage to the eye tissue. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, some additional examinations will be required from related specialists.
Treatment of corneal diseases
Depends on the root cause of the changes. Antifungal and antiviral drugs fight fungi and viruses. Antibiotics – with bacteria. If the disease is caused by tuberculosis or syphilis, anti-tuberculosis therapy is carried out. In case of allergies, all efforts are directed towards searching for the irritant. If contact lenses are the cause of the defect, then switching to glasses is recommended. If vision decreases, corrective optical aids are prescribed.
First aid
If injured, both eyes should be bandaged crosswise. Treat the skin of the eyelids with brilliant green. Place something cold and light on top. Drop Albucid into your eyes. If the pain is severe, take an analgesic. Lie down on the bed.
In case of a burn, you should rinse your visual organs thoroughly with water and saline solution and take a pain reliever.
| If a speck gets in, it is better to leave your eyes alone and not try to remove it yourself. Awkward movements will only do harm. In this case, as in the first two, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. |
Drug treatment
Use:
- anti-infective drugs (Levomycytin, Idoxuridine);
- ointments, drops, antiseptics to suppress inflammation (Albucid, Tetracycline);
- immunosuppressants (Azathioprine, Batriden);
- healing agents (Balarpan, Solcoseryl);
- medications to improve corneal nutrition (Emoxipin).
Therapy for eye injuries
To eliminate injuries, anti-inflammatory drops, ointments, and contact lenses are used to seal the damage. The surgeon sutures through wounds. In case of a burn, the visual organs are washed generously, antibacterial, regenerating, tear-replacing drugs, and anticoagulants are prescribed. In hopeless cases, surgery is performed.
Treatment of the cornea with folk remedies
- Sea buckthorn oil will help speed up the healing process and alleviate symptoms (1-2 drops every hour, duration – 2 weeks).
- They also use the juice of 3-year-old aloe. The plant is wrapped in paper and refrigerated for a week. Then they crush it and squeeze it out. Course – 1 drop once a day for a month.
- In case of suppuration and the formation of a cataract, juice from celandine and propolis is recommended (1:3). 2-3 drops. before bedtime.
- According to healers, honey and royal jelly can get rid of dystrophy. Mix these 2 ingredients 1 to 1. Pour in not hot, boiled water. Place the resulting ointment under the eyelid 3 times a day. For this disease, lotions made from goat's milk, nettle, and lily of the valley are also allowed.
| Herbal treatment is possible in consultation with the doctor. As an auxiliary therapy, folk recipes are quite effective. |
Surgical methods for treating corneal diseases
Operations are performed in severe and advanced cases:
- keratoplasty - replacement of the membrane or part of it with a graft;
- keratectomy – removal of opacities;
- keratoprosthesis – implantation of a prosthesis;
Such operations have been done for a long time. They have good reviews.
Treatment of corneal dystrophy
Conservative and surgical methods are used to treat corneal dystrophy. In the first case, therapy is aimed at slowing the progression of the disease, and in the second, complete elimination of corneal dystrophy is possible.
Important! Dystrophic changes in the membrane of the eye are often irreversible, and the causes of defects cannot be eliminated. Therefore, even radical methods of treating pathology can give temporary results.
Drug treatment
If the course is uncomplicated and there are no signs of rapid progression, the pathology is treated with local and systemic medications. Local medications include:
- Taufon drops to reduce irritation of the eye membrane and protect it from rapid destruction;
- “Emoxipin” drops for regeneration of the corneal layer, stabilization of metabolic processes and strengthening of blood vessels;
- gel "Korneregel", moisturizing, soothing the membrane of the eye, eliminating symptoms.
To reduce symptoms and better protect the surface of the eyes from additional injury and infection, soft contact lenses are used in combination with ointments and gels.
Along with them, systemic drugs are used: injections of aloe extract, lidase and vitreous, vitamin-mineral complexes in the form of tablets and drops, certain types of vitamins intramuscularly.
Surgical operation
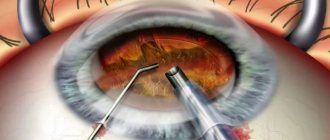
Keratoplasty
- a radical method by which corneal dystrophy is completely eliminated. During the operation, the doctor removes the damaged areas of the cornea layer by layer, and then installs donor or artificial material on the treated areas.
If the damage is superficial, a laser is used to treat corneal dystrophy. The doctor uses it to “evaporate” pathological tissues layer by layer, in place of which new layers are formed.
Prevention of corneal diseases
- Maintain good hygiene . Infections, bacteria, viruses often get into the eyes due to ignoring the rules of cleanliness. Monitor children closely. They love to play in the dirt and touch animals. And when babies want to sleep, what do they do? He rubs his eyes with his hands. It turns out that it is very easy to become infected.
- Do not overdry the cornea . Do not smoke, do not overstrain your eyesight, wear lenses correctly, use glasses to protect against ultraviolet radiation.
- Eat well . Often, a deficiency of vitamins (A, B, B1, E, C) leads to disorders in the cornea. Do exercises for your eye muscles and visit your ophthalmologist regularly.