- Corneal disease
- Cost of services
- Indications and contraindications
- Types and features
- Examination before surgery: tests and preparation
- Requirements for donor material
- Objectives and progress of the intervention
- Postoperative period: rehabilitation
- Possible complications
- Graft rejection
- Where is the best place to have surgery?
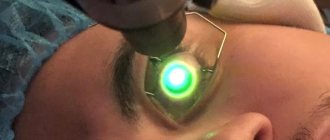
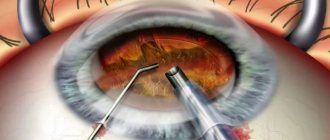
Medicine of the 21st century has achieved serious results, including in the field of ophthalmology. It became possible to carry out organ transplantation, which was previously impossible due to the lack of techniques and medical equipment. We are talking about a surgical intervention called “keratoplasty”. During this procedure, the cornea, which has been altered due to disease or scarring, is replaced with a donor organ or keratoprosthesis. Keratoplasty is a surgical procedure performed using high-precision medical equipment.
Technique of deep layered endothelial keratoplasty
Using a diamond knife, a 5 mm long scleral incision is made at a depth of 400 µm. Stromal dissection is performed using an air bubble in the anterior chamber; the deep layers of the stroma are separated with a dissector. Using a gentian violet trephine trephine, the size of the excised disc is noted on the cornea, after which the patient's corneal disc is excised.
The donor material is prepared in the artificial anterior chamber, then rolled up, placed in a plastic cup, and viscoelastic is applied to the surface of the material. The disc is implanted into the anterior chamber using tweezers, then the bed of the recipient's cornea is compared with the disc of the donor material. The anterior chamber is filled with air for 10 minutes, after which some of the air is removed and replaced with a BSS solution.
Recovery
The eye is kept under a protective bandage for 1 day.
In DMEK, a gas bubble initially persists in the anterior chamber of the eye. The patient sees almost nothing with the operated eye for 5 days to two weeks, only changes in the level of illumination. From about the third week the picture becomes clear, and after a month good vision is already available. The longest, in the case of advanced states of Fuchs' dystrophy, is that you may not see for even a month.
According to our research, in 8% of cases it is necessary to inject a second bubble - if the transplanted layer suddenly begins to come off. The need to do this is determined during examinations after surgery.
As DALK and penetrating keratoplasty (but not after DMEK) heal, wound dehiscence may become a complication. For example, a patient may get into a fight with someone and get punched in the eye. In older people, only a small injury is enough for the connection to burst.
Nylon or mersilene (threads 10/0) are removed as follows: after six months, the first layer, and the second one can take up to 3–5 years, depending on the degree of engraftment. In older people, the second layer is often not removed at all, unless it creates problems; as long as the thread is well tensioned, it does not interfere. It happens that you pull out the second thread and vision decreases, because this thread was the frame of the graft, and this induces astigmatism.
After penetrating surgery or DALK, astigmatism often appears: because even if you sew very well, the scars will depend on healing. The cornea does not heal 360 degrees evenly. After two years, you can do PRK, LASIK or ReLEx SMILE directly inside the graft (I didn’t do the latter myself, but colleagues from Alexandria University have already done it). Another elegant approach to the problem of astigmatism is to replace the lens with a new one if cataract treatment has not yet been performed. If the cataract has been operated on, then a toric backpack lens (Add-on) is placed on the artificial lens - the lens is in front of the primary lens in the capsular bag. If the patient’s own lens is still transparent, the patient is young, and surgery to remove the lens is not needed, then a toric ICL can be placed.
Types of posterior layer-by-layer corneal transplantation
Depending on the layers replaced by the donor cornea and the technique used (keratotome, femtosecond laser), the following are distinguished:
- DLEK (Deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty) - deep layer-by-layer endothelial keratoplasty (endothelial transplantation)
- DSEK (Descemet-striping endothelial keratoplasty) - non-automated endothelial keratoplasty with descemetorhexis
- DSAEK (Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty) - automated endothelial keratoplasty with descemetorhexis (using a microkeratome)
- FS-DSEK (Femto-Second Descemet-stripping endothelial keratoplasty) - DSEK using a femtosecond laser
- DMEK (Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty) - transplantation of Descemet membrane with endothelium
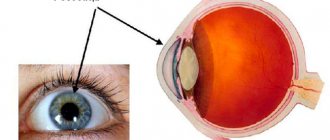
The figure schematically shows:
- A - Structure of the cornea with the designation of layers
- B—through keratoplast (replacement of all layers)
- C - anterior lamellar keratoplasty
- D — anterior layered deep keratoplasty
- E - deep layered endothelial keratoplasty
- A- corneal endothelial transplantation with Descemet's membrane
Cost of keratoplasty
When choosing a clinic, you need to pay attention to those institutions where penetrating keratoplasty is a priority. On average, the cost of a cornea transplant surgery costs from 100,000 to 300,000 rubles per eye.
The package of services includes:
- proven biomaterial that will be used to restore the cornea;
- post-operative care (eye drops, antibiotics, protective eye patches, etc.);
- involvement of an experienced surgeon;
- development of an individual surgical plan for each patient;
- using only modern equipment that does not allow excessive stress on the patient’s cardiovascular system;
- selection of anesthesia that is well tolerated by patients;
- discharge only after a follow-up examination by a surgeon;
- postoperative examinations and consultations;
- urgent medical care in case of complications.
In 90% of cases, keratoplasty can achieve a significant improvement in visual function. Only a few patients develop complications, most of which can be easily controlled with medication.
Sources used:
- Crutchmer, Jay Rogowitz. Atlas / Jay Crutchmer, David Paley. - M.: Logosphere, 2007.
- Olga, Krivosheina and Igor Zapuskalov Modern pharmacotherapy of ulcerative lesions of the cornea: monograph. / Olga Krivosheina and Igor Zapuskalov. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- Stepanov V.K., Murieva I.V., Isaeva O.V. Therapeutic corneal transplantation. Bulletin of Orenburg State University, 2015
- Wikipedia article
Benefits of the operation
An important advantage of this intervention is the presence of irregularities on the inner surface of the cornea, which form after its dissection, which reduces the likelihood of transplant rejection.
Posterior lamellar keratoplasty, performed with the removal of Descemet's membrane, is characterized by a minimal degree of astigmatism induced by the operation and less trauma to the eyeball. Endothelial corneal plastic surgery is pathogenetically more justified in the case of endothelial-epithelial corneal dystrophies of various origins.
In addition to such obvious advantages of endokeratoplasty as its pathogenetic validity, the absence of corneal sutures, the “closed palate” technique, which reduces the likelihood of complications associated with sagging sutures, opening of the eyeball, and infectious complications, it is also important to have the ability to accurately calculate the diopter of the implanted intraocular lens ( if keratoplasty is performed simultaneously with cataract extraction).
The technical feasibility of receratoplasty in the early postoperative period is also important. The risk of needing re-plasty in case of failure of the end-to-end graft is reduced. When there is a lack of donor material, it is important to be able to use one donor eye to perform three surgical interventions (anterior lamellar keratoplasty, endokeratoplasty, allolimbal transplantation).
The length of stay of patients in the hospital is reduced, rehabilitation is achieved in the shortest possible time with a significant improvement in the quality of life of patients. The intensity of therapy in the postoperative period is reduced, including the use of expensive drugs.
Indications for corneal transplant surgery
Among all diseases of the visual system, pathologies of the corneal layer make up a quarter. Often, corneal diseases provoke irreversible deterioration in visual function. The danger of pathologies of this part of the eye is that most of them cannot be corrected with glasses and contact lenses. For this reason, keratoplasty is considered practically the only way to restore vision to patients with corneal clouding or changes in its sphericity.
Indications for corneal transplantation:
- keratoconus (non-inflammatory pathology in which the cornea takes on a conical shape and gradually thins);
- keratoglobus (non-inflammatory pathology in which the corneal stroma thins and protrudes, which leads to its globe-shaped deformation);
- avascular corneal cataract (clouding that occurs due to injury, inflammation, chemical or thermal burn, complication of keratitis or ulcer);
- post-traumatic scars (the result of inflammation or surgery);
- corneal dystrophy (congenital or acquired).
Before keratoplasty, as before any other surgical procedure, the patient must undergo an examination. It will allow you to identify all indications and contraindications, identify risk factors, and predict the results of the procedure.
Contraindications to keratoplasty:
- entropion (inversion of the eyelid, in which the edge of the eyelid and eyelashes come into contact with the cornea and conjuncture of the eye and irritate them);
- ectropion (eversion of the eyelid, in which the contact of the eyelid and the eyeball is disrupted, the mucous membrane of the eye is exposed);
- blepharitis (a group of diseases that provoke chronic inflammation of the eyelid);
- bacterial keratitis (acute inflammatory process in the cornea, which is of a bacterial nature).
If these or other contraindications are detected, full treatment must be carried out, followed by a re-examination and surgery (if there are no diseases).
Cost of operations
In our ophthalmology center, it is possible to perform all types of posterior lamellar keratoplasty (DLEK, DSEK, DSAEK, FS-DSEK and DMEK) using the most modern equipment, incl. leading ophthalmologists in Germany who come to Moscow for consultations and operations.
The price for endothelial keratoplasty is from 300,000 rubles, which is significantly lower than the cost of similar operations in Europe and, especially, in Israel.
The material was prepared by an ophthalmologist: Sagonenko Dmitry Alekseevich
You can ask clarifying questions and make an appointment at our clinic online or by phone in Moscow: Diagnosis and surgical treatment of keratoconus Selection of hard scleral contact lenses.
Indications for performing penetrating keratoplasty
Penetrating keratoplasty surgery may be prescribed when irreversible changes in the structure of the cornea occur due to infectious, traumatic or dystrophic damage. It is especially often carried out in the following cases:
- Progressive corneal dystrophy with its edema in bullous keratopathy
- Corneal ulcers due to various types of infection
- Traumatic changes in the cornea
- Keratoconus
- Corneal scars
- Fuchs' dystrophy
- Corneal burns
Important! Our clinic performs all types of keratoplasty, and not just penetrating keratoplasty (as in many other ophthalmological centers in Moscow). For you, this means that if it is possible to perform a gentle operation that gives much better results - layer-by-layer anterior or posterior transplantation - then our doctors will recommend it, and will not insist on a complete cornea transplant! Get a consultation from our ophthalmologists and choose the best method that will preserve your vision.
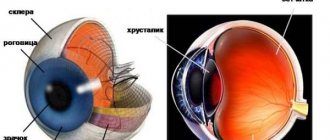
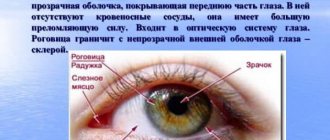
Corneal diseases
Corneal diseases occur in 25% of patients visiting an ophthalmologist. The cornea is the transparent membrane of the eye, 10-12 mm in diameter, which, like a watch glass, covers the colored structure of the eye called the iris.
A decrease in the transparency of the cornea, leading to loss of vision, can be due to many reasons: burns and eye injuries, keratitis and corneal ulcers, primary and secondary corneal dystrophies, keratoconus and keratoglobus. These corneal injuries and diseases require surgical treatment.
DIAGNOSIS OF CORNEA DISEASES
TREATMENT
In the surgical treatment of corneal diseases, two main directions can be distinguished: keratoplasty (corneal transplant), when the damaged cornea is replaced with healthy donor corneal tissue, and keratoprosthesis - transplantation of an artificial cornea.
MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" has the most experience in Russia in performing keratoplasty: over 30 years of work, over 16,500 donor cornea transplants have been performed. The Eye Microsurgery MNTK operates the largest and most modern Eye Bank in Russia with the latest medical and technological support. The complex is the only medical institution in Russia where the keratoprosthesis method is widely used, using its own models of keratoprostheses.
Keratoplasty surgery is performed on patients with keratoconus, corneal dystrophies, corneal opacities, etc.
| Keratoplasty | The total treatment time for one eye is 14-21 days (preoperative examination 2-3 days, on the 4th day - surgery ( the timing of the operation depends on the availability of donor material ), postoperative follow-up treatment - 10 days) |
To treat corneal cataracts, keratoprosthesis surgery is performed.
| Keratoprosthetics | The total treatment time for one eye (one stage) is 5 days (stage 1: strengthening the cataract and implanting support elements, preoperative examination 2 days, surgery on the 2-3rd day, postoperative observation - 1-2 days; 2nd stage implantation of a keratoprosthesis (3-4 months after the 1st stage).The duration of the operation is the same as at the 1st stage. |
Keratoplasty and keratoprosthetic operations are performed on an inpatient basis and usually take from 30 minutes to 1 hour. In the operating room you will be accompanied by a surgeon, his assistant, an operating room nurse, an anesthesiologist and a nurse anesthetist. Modern methods of anesthesia used in the MNTK “Eye Microsurgery” make it possible to completely eliminate pain.
The operations are performed by highly qualified surgeons from the Department of Transplantation and Optical Reconstructive Surgery of the anterior segment of the eyeball using the most modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers.
, new technologies for the surgical treatment of corneal dystrophy and keratoconus have begun to be widely used at the Eye Microsurgery International Scientific and Research Center .
- Deep anterior layer keratoplasty, which allows you to preserve your own healthy endothelium and avoid opening the eyeball (depressurization), reduce surgical and postoperative complications and the risk of graft rejection.
- Posterior lamellar endothelial keratoplasty, intended for the treatment of corneal dystrophy, allows the portion of donor tissue to be minimized, which reduces the risk of rejection and preserves most of the native cornea.
- Reconstruction of the anterior segment of the eyeball with implantation of an artificial iris based on penetrating keratoplasty in cases of severe corneal trauma combined with loss of the lens and iris.
- An alternative to penetrating keratoplasty for initial and advanced stages of keratoconus is introstromal keratoplasty with implantation of segments. The operation is performed in the early stages of keratoconus, has an orthopedic function, strengthens the thinned area, improves visual acuity, and stops the progression of keratoconus.
- Cross-linking of corneal collagen (cross-linking) slows or stops the progression of keratoconus based on biochemical remodeling of the cornea.
Improvements in microsurgical techniques and instruments, the emergence of new advanced equipment, and new approaches to pre- and postoperative therapy have expanded the range of surgical interventions on the cornea and provided a large percentage of favorable outcomes and high results.
MODERN METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF KERATOCONUS
KERATOCONUS
Keratoconus is a progressive dystrophic disease of the cornea, caused by a number of genetic and acquired factors, characterized by progressive thinning of the cornea with protrusion of its central parts, the formation of myopic refraction and irregular astigmatism. The etiology of keratoconus and other types of keratoectasias is currently unknown. Active progression of keratoconus occurs in 20% of cases and, as a rule, begins during puberty. The progression of the disease leads to a significant decrease in visual acuity and the ineffectiveness of methods for its correction. Making a diagnosis, especially in the initial stages of the disease, is very difficult. The most informative study at the moment in diagnosing this terrible disease, along with generally accepted research methods, is the performance of a scanning keratotopograph PENTACAM (OCULUS, Germany), which makes it possible to evaluate both the anterior and, most importantly, the posterior surface of the cornea - since this is where the initial anatomical changes occur. topographic characteristics in the initial stages (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Scanning keratotopograph PENTACAM (OCULUS, Germany).
Treatment of keratoconus
Depending on the stage of the disease and some important anatomical and topographical characteristics, the ophthalmic surgeon, based on many years of experience and the latest scientific developments of the Eye Microsurgery Institute, will offer the optimal treatment method. There are three main treatments for keratoconus:
Crosslinking of corneal collagen (Fig. 2)
The idea of using a conservative method of treating keratoconus was born in Germany by a group of researchers at the Technical University of Dresden. T. Seiler and G. Wollensak took as a basis the principle of photopolymerization, which has long been used in dentistry (“light filling”). As a result of a series of works, the most effective and safe technique for cross-linking corneal collagen was developed, based on the effect of photopolymerization of stromal fibers under the influence of a photomediator (riboflavin solution) and low doses of ultraviolet radiation from a solid-state source. This technique makes it possible to stop the progression of keratoconus and avoid end-to-end corneal transplantation.
Rice. 2. Crosslinking of corneal collagen
Indications:
- Keratoconus stages I-II.
- Keratoectasia after refractive excimer laser interventions.
- Corneal marginal degeneration
- Keratomalacia of various origins - cornea melting, usually during autoimmune processes.
- Keratoglobus.
- Bullous keratopathy stages I-II.
- There is encouraging data on the use of cross-linking in the treatment of keratitis and corneal ulcers.
Contraindications:
- Intolerance to Riboflavin (Vitamin B2).
- If the thickness of the cornea in at least one dimension is less than 400 microns.
- Age less than 15 years
- Low corrected visual acuity in keratoconus, despite sufficient thickness.
- Presence of corneal scars.
- The presence of allergic conjunctivitis.
Implantation of intrastromal corneal segments
In our practice, we use domestic IRS manufactured at Scientific and Experimental Production LLC "Eye Microsurgery" from polymethyl methacrylate, which is a segment with an arc length of 160 ° (90, 120, 160, 210 °), base 0.6 mm, height 150 - 450 µm, internal diameter 5.0 mm and external 6.2 mm, with a hemispherical cross section (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Intrastromal corneal segment
Correction of keratoconus and high-degree complex myopic astigmatism. First, a corneal tunnel is formed in the cornea, through which a corneal segment is inserted, which leads to flattening of the central zone of the cornea. An important aspect of this operation is its reversibility – i.e. the possibility of replacing or removing a segment if vision changes with age. This is possible because the center of the cornea is not damaged and no corneal tissue is removed. The next day after the operation, the patient’s eye is absolutely calm and after a short rehabilitation the patient can resume everyday visual stress (Fig. 4 It should be noted that implantation of intrastromal segments does not affect the patient’s cosmetics and allows him to use soft contact lenses. Depending on the indications, a combination is possible cross-linking and introstromal implantation of corneal segments.
Rice. 4. Patient's eye the day after implantation of the corneal segment
3.Keratoplasty
Recently, the method of choice for surgical treatment of keratectasia in advanced stages of the disease has often become anterior deep lamellar keratoplasty, during which the corneal stroma is peeled off from Descemet's membrane. At the same time, the increase in visual acuity is comparable to that after penetrating keratoplasty. The advantages of anterior deep lamellar keratoplasty over penetrating keratoplasty are: preservation of the endothelium of the recipient's cornea, which reduces the risk of graft rejection; reducing the risk of developing cataracts in the postoperative period due to the administration of a shortened course of steroid therapy; reducing the requirements for the donor graft, since the quality of its endothelium in this case does not play such a significant role as in penetrating keratoplasty.
It should be noted that the best results can be obtained when performing keratoplasty - both penetrating and anterior deep layer-by-layer with the use of femto-laser support, which ensures ideal cutting accuracy and unsurpassed compatibility of the cut donor graft and the recipient bed, leading to a significant increase in the visual functions of patients . Thus, currently, a qualified ophthalmic surgeon has a wide range of surgical methods for treating keratoconus. However, it should be noted that the most effective treatment is considered to be in the early stages of the keratectic process, which is possible with timely correct diagnosis of the keratectasis. The most effective modern methods for early diagnosis of the keratecstatic process are: computer keratotopography, optical coherence tomography, confocal scanning microscopy, immersion confocal microscopy, analysis of elevation maps. Our institute is equipped with the most advanced equipment for the early diagnosis of keratoconus, which allows us to detect keratoconus, even at the earliest stages of development, in 100% of cases. It should also be noted that the abundance of different methods for treating keratoconus poses the task of choosing the most effective method of treatment for each individual patient. The leading specialist of our institute is Doctor of Medical Sciences. Svetlana Borisovna Izmailova, based on a comprehensive analysis of the results of treatment of patients with keratoconus, developed an algorithm for the surgical treatment of keratoconus, which allows systematizing approaches to the treatment of keratoconus and differentially selecting the most optimal and effective method of treatment depending on the stage of the disease. Thus, the MNTK “Eye Microsurgery” presents the entire range of modern therapeutic and diagnostic technologies, allowing pathogenetically oriented treatment for each patient with keratoconus at any stage - from initial to acute. We can help everyone!
Our specialists:
Malyugin B.E. – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor. Performs operations on mechanical and femtolaser implantation of corneal segments, various types of keratoplasty, including layer-by-layer. Proficient in technologies for intraocular correction of residual myopia and astigmatism in patients with stabilized keratoconus.
Izmailova S. B. – Doctor of Medical Sciences Performs implantation of corneal segments, including femto-assisted, UV cross-linking, penetrating and lamellar keratoplasty - mechanical and femto-laser assisted. Proficient in technologies for intraocular correction of residual myopia and astigmatism in patients with stabilized keratoconus.
Kostenev S.V. – Doctor of Medical Sciences Performs implantation of corneal segments with femto-laser assistance and UV crosslinking. Performs PRK to correct residual ametropia.
Kovshun E.V. – Ph.D. He specializes in the treatment of advanced stages of keratoconus using penetrating and lamellar keratoplasty, and performs implantation of corneal segments and UV crosslinking.
Volkova O.S. – Ph.D. Performs implantation of corneal segments, including with femto-laser assistance, and penetrating keratoplasty.
Golovin A.V. – Ph.D. Performs femto-laser implantation of corneal segments.
Pashtaev A.N. – Ph.D. Performs femto-laser implantation of corneal segments.
Moroz O.V. – Performs implantation of corneal segments.
Contact us! We will help you!
YOUR DOCTORS
Types of keratoplasty
There can be several types of surgical manipulations with the cornea, because... The tissue itself is not homogeneous (the cornea consists of five layers, although some researchers identify six) and its various parts can be affected. In some cases, the applicability of the term “corneal transplant” is not discussed at all. Let's figure out what options are possible.
Integumentary (therapeutic) keratoplasty
The meaning of this operation is to cover the inflamed cornea from the outside with either its own tissue (conjunctiva) or foreign tissue - for example, amnion, in order to prevent perforation of the eye and localize the pathological process. There is no donor (cadaveric) cornea here.
Through transfer
In this type of operation, the patient's cornea is replaced with donor tissue completely to its full depth (“through and through”).
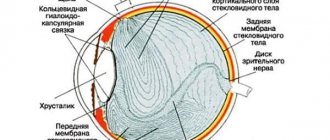
Layer keratoplasty
In this case, only part of the cornea changes. These can be outer layers - to different depths (anterior deep layered keratoplasty or DALK) or internal layers (posterior layered keratoplasty (endothelial) - DSEK or DSAEK).
In addition, manipulations in the thickness of the cornea are possible - this is lamellar intrastromal keratoplasty (when the cornea is delaminated and donor material is placed inside, thus strengthening the patient’s tissue). In our center, it is most popular for patients with keratoconus and is performed according to the author’s technique.
Appearance of the patient's eye after posterior lamellar keratoplasty (endothelial) for Fuchs syndrome
Keratoprosthetics
In some cases (due to the condition of the eye or the lack of donor material for transplantation), prosthetics of a portion of the cornea is performed using artificial prostheses. As a rule, they are a piece of polymer material that can be sutured to the patient's tissues.
Installation of such a keratoprosthesis allows to some extent improve visual acuity and improve a person’s quality of life. As a rule, this is a temporary phenomenon, but in older and sicker patients such an implant may remain for life.
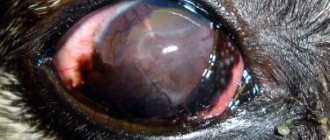
The appearance of the eye of a patient with a keratoroprosthesis - the vessels in the native cornea are visible, due to which transplantation of a donor cornea is impossible
Femtosecond keratoplasty
In fact, this is not some separate type of corneal plastic surgery, but its technical implementation. With this type of operation, instead of special keratomes (“cornea knives”), a femtosecond laser is used, which cuts out tissue fragments (both the graft and the patient’s cornea) of the required size. However, in some cases, due to the characteristics of the patient's tissue or surgical technology, the use of a femtosecond laser can be difficult.
You can find out more about each type of surgical treatment in the corresponding section.
Preparation for keratoplasty
After making a decision about keratoplasty, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, and possible contraindications are identified. The patient is then placed on a waiting list and a suitable cornea is selected. The waiting period is individual for each patient.
If the patient has inflammatory and infectious diseases of the cornea, they must first be cured. Decompensated conditions negatively affect the survival rate of the donor graft and the outcome of corneal transplantation.
On the eve of the intervention, the doctor gives recommendations on preoperative medication, with special attention paid to anticoagulants and antiplatelet therapy. On the day of surgery you need to be on an empty stomach. Most often, such an operation is performed in a hospital setting, that is, after the patient’s preliminary hospitalization in the clinic, but it can also be performed on an outpatient basis.
How is keratoplasty performed at the Excimer Clinic?
During the operation, the surgeon uses a microsurgical instrument or a femtosecond laser to create a corneal flap and separate the damaged part of the cornea. In its place, “Material for corneal restoration” is implanted, which exactly matches the size of the previously formed flap. Using a special suture material, it is attached to the peripheral part of the patient's cornea. After the operation is completed, a bandage or a special protective contact lens is applied to the patient's eye.
Keratoplasty at the Excimer clinic is performed in a “one-day” , under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. After the operation and examination by a doctor, the patient returns home. The rehabilitation period after keratoplasty lasts up to a year due to the structural features of the cornea. During this period, the patient is regularly observed by the attending physician at the Excimer clinic, who monitors the dynamics of recovery. Suture removal usually occurs 6 to 12 months after surgery. After keratoplasty, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical activity and physical impact on the operated eye.