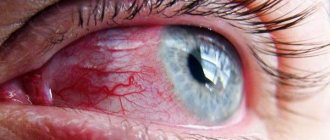
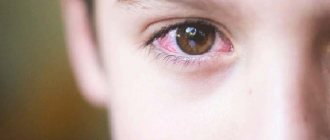
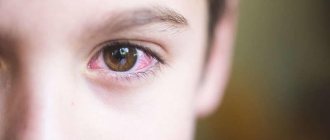
Conjunctivitis is a common disease in childhood, but many parents often underestimate the severity of the disease and rarely seek help from specialists. Subsequently, this can only aggravate the situation and prolong the disease. From this article you will learn about the symptoms of the disease, how long it lasts, and how to speed up the recovery process.
Share
Tweet
Share
Cool
Send
What kind of disease is this?
Conjunctivitis is a group of ophthalmological diseases in which inflammation occurs on the connective membrane of the eye - the conjunctiva. The connective membrane has a protective function and provides hydration to the eyeball, so any inflammation on it can be not only painful, but also dangerous for the eye itself.
Conjunctivitis can occur at different ages, but children suffer from this disease more severely than adults. Young children may have problems with their appetite or sleep, and they become irritable and moody.
One of the main factors contributing to the development of the disease is poor hygiene. In preschool age, it becomes more difficult for adults to control children: kids may play with dirty toys or dig in the sand, and then touch their eyes. This is how microbes become pathogens. At the same time, conjunctivitis is often epidemic in nature, so several children can become infected at once.
Conjunctivitis is an extremely common disease among ophthalmic pathologies. With full treatment with special medications prescribed by a doctor, the disease goes away quickly and does not cause complications. However, if treatment is delayed, serious complications may develop, resulting in loss of visual acuity and even sepsis.
Types and causes of occurrence
There are 3 types of conjunctivitis in children:
- Viral. Occurs less frequently than others. Occurs against the background of other diseases, such as acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis or runny nose. Most often, only one eye is affected, but if the disease starts, it will spread to the second eye. During the normal course of the disease (without complications), a clear liquid is released from the eyes. If bacterial conjunctivitis is added to viral conjunctivitis, the discharge will turn yellow. It is observed in the autumn-spring period, when children's immunity decreases. Often the disease begins with a high body temperature. If only one eye is affected, the disease is most likely caused by the herpes virus.
- Bacterial. The causative agents are pneumococci and staphylococci. Most often, the bacteria enters the eye due to poor hand hygiene. Moreover, the bacterium can remain on the mucous membrane for a long time without signs of illness, and develop only when the baby’s immunity declines. This type of conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes at once. When affected, the eyelids become swollen, pus is released, and it is difficult to open the eyes in the morning.
- Allergic. The disease manifests itself as a response to an allergen - cat hair, pollen, medications, etc. It develops at lightning speed - within fifty minutes after contact with the allergen. This type of conjunctivitis cannot be contracted from another person. Both eyes are affected at once, the eyelids begin to itch severely, and there is no purulent discharge. There are 4 types of allergic conjunctivitis:
- Seasonal. As a rule, it occurs in the spring, when abundant flowering begins outside. It is difficult because it is often very difficult to remove the allergen. Even ordinary ventilation can turn into torture for a child with this form of allergy.
- Year-round. Occurs if the allergen is always near the baby (cat hair, bird feathers, etc.). This type of conjunctivitis can be avoided if you always isolate the allergen from the child.
- Giant papillary. Formed due to a foreign body that can enter the eye.
All of the above forms of the disease are classified as acute. But there is also a chronic form of the disease.
Chronic conjunctivitis is difficult to treat and has two stages of the disease - exacerbation and remission. With chronic conjunctivitis, the cornea of the eye becomes cloudy, and persistent discomfort in the eye persists. Inflammation of the eye in a chronic form leads to the fact that the child begins to tire quickly, becomes very irritable, and visual acuity is lost.
Causes
The cause of viral conjunctivitis is the penetration of the following pathogens into the mucosa:
- adenoviruses;
- herpes simplex virus;
- enteroviruses;
- pathogens of influenza, measles, rubella, chickenpox;
- molluscum contagiosum.
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! Viral conjunctivitis most often develops against the background of colds. For example, with FLU, tonsillitis and runny nose. How many days conjunctivitis lasts in children depends on the state of the immune system and concomitant diseases.
If the pathogen is an allergen
This form of conjunctivitis is a response to contact with an allergen. Divided into the following types:
- Seasonal. Flowering plants become provocateurs. It’s difficult to say how long it will take for this disease to go away, because... Treatment consists of preventing contact with the allergen. This is quite problematic to do in spring and summer, because... pollen can get in during a walk or even when airing a room.
- Year-round. In this case, the provocateurs are wool, dust, feathers, food, etc. How long it takes to treat conjunctivitis depends on how quickly you can eliminate contact with histamine. For example, if you are allergic to dust, you need to carry out wet cleaning daily, preferably several times a day.
- Giant papillary. Occurs as a result of penetration of a foreign object into the eyes, triggering an allergic reaction.
How long the incubation period lasts depends on the individual characteristics of the child. That is, his predisposition to an allergic reaction. As a rule, no more than 15-30 minutes elapse between contact with histamine and the first symptoms.
Bacterial pathologies
The causative agents of this form are pneumococci and staphylococci. Bacteria can enter the body due to poor hygiene.
Rapid development should not be expected. Incubation can last a long time, several weeks or even months. Pathogens will begin their active development when the immune system is weakened.
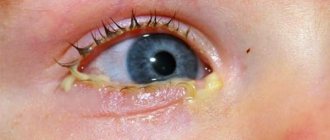
Rice. 2. What does bacterial conjunctivitis look like?
How does infection occur?
As a rule, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye is preceded by a disease that weakens the immune system. This could be microtrauma to the eye, contact with the mucous membrane of chemical irritants, or a disease not related to the eyes, but which greatly affects the child’s general immunity - acute respiratory infections, severe poisoning, etc.
Infection with bacterial conjunctivitis occurs due to neglect of hand hygiene. Usually the child picks up the contaminated object, and after a few seconds rubs his eyes with his hands. As a result, bacteria penetrate the mucous membrane and can manifest themselves both immediately and after some time, when the child’s immunity weakens.
The baby may also contract conjunctivitis during birth. Passing through the birth canal, the bacterium can penetrate the mucous membrane of the child’s eye and, with improper subsequent care, develop into conjunctivitis.
Types of conjunctivitis
The disease is divided into several types and each of them has its own symptoms and different treatment.
Allergic – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye in response to irritation by allergens. An allergic reaction can be caused by: flower and tree pollen, house mites, animal hair, household chemicals and medications. The child feels a burning sensation in the eyes, redness, tearing and swelling appear.
Viral - develops along with ARVI, the causative agent is a viral infection, enters with dirty hands or through the blood. Reduced immunity contributes to the development of the disease. It manifests itself as inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, redness, lacrimation, and slight purulent discharge. The form of the disease is mild and can be treated within a few days.
Adenoviral - this type of conjunctivitis usually causes fever, redness of the eyes, and watery eyes. Children suffer from it mainly in the spring, the source is an adenoviral or bacterial infection.
Bacterial - the source of this type of disease is bacteria, develops after injury, infection in the tear duct. It is characterized by burning eyes, a gritty sensation, and sticky discharge that sticks the eyelids together after sleep.
Purulent - develops when microbes are introduced from the outside. It could be debris, a small insect, or an infection. Characterized by the formation of pus, inflammation of the mucous membrane, dilation of blood vessels, itching in the corners of the eyes.
Stages of development
- Incubation period. The duration depends on the type of conjunctivitis. If the cause is a virus, then on average the incubation period lasts 8 hours. Bacterial conjunctivitis can manifest itself almost immediately after bacteria enter the mucous membrane.
- First stage (acute form). General weakness, possible fever. Lasts 1-3 days. At this time, redness of one or two eyes occurs at once. The child may be capricious and refuse to eat. If the baby is very small, then the onset of the disease can be suspected not only by restless behavior, but also by constant scratching of the eyes with his fists.
- Second stage (subacute form). The disease begins to recede. If treatment is started on time, the second stage will end with complete recovery. If treatment is not provided, the disease becomes chronic.
Reference. A relapse of the disease may occur. Most often, it is children who are susceptible to re-infection immediately after recovery. The reason for this is weakened immunity.
Conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis in a child can occur in isolation; in some cases the ocular symptoms are preceded by catarrhal symptoms. With conjunctivitis of any etiology, children develop a symptom complex, including swelling of the eyelids, conjunctival hyperemia, increased lacrimation, fear of light, foreign body sensation or pain in the eyes, blepharospasm.
In children, an eye infection can be suspected even before clinically significant manifestations appear due to restless behavior, frequent crying, and constant attempts to rub their eyes with their fists. With isolated conjunctivitis in children, the body temperature is usually normal or subfebrile; in case of general infection it can rise to high values.
Due to the thickening of the conjunctiva and its injection by blood vessels during the disease, visual function is slightly reduced. This deterioration is temporary and reversible: with adequate treatment of conjunctivitis, vision is restored immediately after the children recover.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in children
With conjunctivitis of bacterial etiology, eye damage is bilateral, often sequential - first the infection manifests itself in one eye, and after 1-3 days the other eye is affected. A typical sign of bacterial conjunctivitis in children is mucopurulent or viscous purulent discharge from the conjunctival cavity, sticking of the eyelids, and drying of crusts on the eyelashes. The color of the conjunctival discharge can vary from light yellow to yellow-green.
The course of bacterial conjunctivitis in children can be complicated by blepharitis and keratoconjunctivitis. Deep keratitis and corneal ulcers develop rarely, mainly against the background of a general weakening of the body - hypovitaminosis, anemia, malnutrition, bronchoadenitis, etc.
Gonoblenorrhea of newborns develops 2-3 days after birth. Symptoms of conjunctivitis of gonorrheal etiology are characterized by dense swelling of the eyelids, bluish-purple coloration of the skin, infiltration and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, serous-hemorrhagic, and then profuse purulent discharge. The danger of gonococcal conjunctivitis in children lies in the high likelihood of developing purulent infiltrates and corneal ulcers that are prone to perforation. This can lead to the formation of a cataract, a sharp decrease in vision or blindness; when infection penetrates into the internal parts of the eye - endophthalmitis or panophthalmitis occurs.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis in children develops 5-10 days after birth. At older ages, infection can occur in closed reservoirs, and therefore outbreaks of the disease in children are often referred to as basin conjunctivitis. The clinical picture is characterized by hyperemia and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the eyelids, ptosis of the eyelids, the presence of abundant liquid purulent secretion in the conjunctival cavity, and hypertrophy of the papillae. In children, extraocular manifestations of infection are often possible: pharyngitis, otitis, pneumonia, vulvovaginitis.
Diphtheria conjunctivitis usually develops against the background of diphtheria of the pharynx, mainly in children under 4 years of age. It should be noted that currently, thanks to mandatory vaccination of children against diphtheria, isolated cases of infection are observed. Eye damage is characterized by painful swelling and hardening of the eyelids, which, when opened, release a cloudy serous-hemorrhagic secretion. Gray, difficult to remove films are visible on the surface of the conjunctiva; after their removal, the bleeding surface is exposed. Complications of diphtheria conjunctivitis in children may include infiltrates and ulcerations of the cornea, clouding of the cornea, perforation of the ulcer and death of the eye.
Viral conjunctivitis in children
Viral conjunctivitis in children usually accompanies the course of ARVI, and is therefore characterized by a temperature reaction and catarrhal symptoms. In this case, the involvement of the eyes in inflammation occurs sequentially. Viral conjunctivitis in children is characterized by copious, liquid, watery discharge from the conjunctival sac, giving the impression of constant lacrimation.
With herpetic conjunctivitis in children, rashes in the form of blisters may be found on the skin of the eyelids and conjunctiva; with measles conjunctivitis - a measles-like rash; with chickenpox - smallpox pustules, which, after opening, turn into scars. Sometimes viral conjunctivitis in children is complicated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which is accompanied by the appearance of purulent discharge from the eyes.
Symptoms
Most often, childhood conjunctivitis develops gradually. Here are a few signs by which you can identify the disease:
- Discomfort in one or both eyes, strong desire to rub the eyes.
- Burning of eyelids.
- Visual fatigue.
- Photosensitivity.
- Purulent or clear discharge.
- "Gluing" of the eyes after sleep.
- Dry crusts in the corners.
- Redness and swelling of the eyelid.
- Pain when blinking.
- Visual impairment.
Children become very restless and lose their appetite. If it is viral conjunctivitis, there may be an increase in body temperature.
If the disease is present, not all of the above symptoms may be present. But if you find at least 2-3 symptoms in your child, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
The disease is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. To establish a diagnosis, the doctor performs an ophthalmological examination and prescribes tests.
The doctor's examination includes examination of the eyelids with side lighting, as well as biomicroscopy (examination of the eyeball using a special three-mirror Goldmann lens).
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
If conjunctivitis is suspected and there is no purulent discharge, the doctor may prescribe a cytological examination of a smear from the connective membrane of the eye, as well as bacteriological, immunological and serological studies. Examinations are often prescribed to determine the likelihood of helminthic infestation or dysbacteriosis.
An additional appointment with an allergist and immunologist may also be scheduled.
If all signs indicate that the child has allergic conjunctivitis, the doctor will prescribe skin allergy tests to identify the allergen.
General principles of treatment
Because bacterial and viral conjunctivitis are contagious, you should immediately isolate the sick child from other children.
Therapy is prescribed only by a doctor. Self-medication of childhood conjunctivitis is not recommended.
Under no circumstances should you:
- Apply any compresses to your eyes.
- Tape or blindfold.
All this can lead to a worsening of the disease, since a closed environment can create conditions for the proliferation of bacteria and the spread of infection not only through the conjunctiva, but also into the cornea.
What you can and should do before seeing a doctor:
Treat eyes every 2-3 hours. At the same time, cotton swabs for treatment need to be changed constantly; there should be one for each eye. The procedure is carried out in the direction from the outer corner to the inner. Even if inflammation is present in only one eye, treatment should be carried out on both. What can you do to treat your eyes:
Duration of conjunctival inflammation
Conjunctivitis in children is treated faster than in adults. The duration of inflammation depends on the type and causes of the disease.
Bacteriological conjunctivitis:
- Staphylococcal infection can last 5-6 days.
- Pneumococcal – 13-15 days.
- Gonococcal (most often found in newborns) – up to two months.
- Chlamydial – 15 days until complete recovery.
Viral conjunctivitis is extremely dangerous and contagious. Its treatment can last from 7 days to two months (depending on the severity of the disease and the presence of complications).
The allergic form disappears 10-14 days after isolating the allergen.
An essential factor for a quick recovery is timely consultation with a doctor. Self-medication can not only delay the entire recovery process, but also lead to serious complications, which can subsequently cause poor vision in the child.
Duration of bacterial conjunctivitis
There are bacterial conjunctivitis: nonspecific, pneumococcal, gonococcal, chlamydial, diphtheria, etc.
Nonspecific inflammation is most often caused by staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Inflammation begins with damage to both eyes; pronounced conjunctival injection, swelling and pronounced purulent discharge from the conjunctival cavity appear acutely. With all nonspecific infections of the conjunctiva, the inflammatory process may not be limited and spread to the cornea (with the development of keratitis). If you seek help early and receive adequate treatment, the disease goes away in 6 to 7 days.
Pneumococcal conjunctivitis is caused by diplococci, infection occurs through household contact. An acute disease begins with swelling of the transitional fold, then after 1–2 days a delicate whitish-gray film appears on the conjunctiva of the eyelids. Pneumococcal conjunctivitis is treated similarly to streptococcal and staphylococcal infections. The duration of therapy is 7 – 10 days.
All people who were in contact with the patient should instill a 20% solution of sulfacetamide into the eyes for 2-3 days.
Gonococcal conjunctivitis can develop in newborns during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal of a sick mother, or in adults, if personal hygiene rules are not observed, the infection is carried into the eyes with contaminated hands. It does not develop immediately, but on days 2-3 from the appearance of bluish-purple swelling of the eyelids. In this case, the eyelids become dense, swollen, and the patient cannot open his eyes well. A discharge the color of meat slop pours out of the palpebral fissure. After 3–4 days, the swelling of the eyelids subsides. Full recovery occurs in 1.5 – 2 months. Without treatment, further progression can lead to loss of the eye.
How many days is an eye infection contagious in a child?
Bacterial conjunctivitis spreads very quickly from person to person. Therefore, the child is considered contagious until recovery. In the case of a viral type of disease, it is not the conjunctivitis itself that is dangerous, but the virus that caused it, therefore the period when a child is considered contagious depends on the type of general disease.
How to speed up recovery?
Here are some recommendations that will help significantly speed up your child’s recovery:
- It is necessary to carry out hygiene of the child’s hands as often as possible, including with special aseptic means.
- It is necessary to ensure the timely change of individual accessories and household items (towels, bed linen, toothbrushes, etc.)
- Under no circumstances should you apply compresses to your eyes or cover them with bandages.
- Teenagers should not use decorative cosmetics and products for the skin around the eyes and face during illness.
- It’s worth stopping wearing lenses for a while.
- Do not use eye drops for more than the time prescribed in the instructions.
- Treat the child's eyes with chamomile solution or a weak solution of furatsilin as often as possible.
Complications and consequences
If treatment for conjunctivitis in a child is not started in time, the disease can become chronic and will be much more difficult to cure.
Complications that may occur as a result of improper treatment of the inflamed connective membrane of the child’s eye:
- Blepharitis. This is an inflammation of the eyelids caused by a bacterial infection. As a rule, blepharitis is chronic and very difficult to treat.
- A cataract or clouding of the cornea. May lead to decreased visual acuity.
- Keratitis. This is an inflammation of the cornea. The disease can lead to visual impairment. It is characterized by photophobia, tearfulness and the appearance of a “veil” in the eyes.
- Dry eye syndrome. Inability to produce tears. Often this disease can occur in older people, but it can also appear in childhood if infectious conjunctivitis occurs.
- Hypopyon. The disease is characterized by the accumulation of purulent formations in the lower part of the eyelid. In advanced stages, hypopyon is treated with surgery.
- Sepsis. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream and lead to blood poisoning.
- Otitis media Every fourth child with an advanced form of conjunctivitis is diagnosed with otitis media.
How long does conjunctivitis last in children and adults?
- October 24, 2018
- Ophthalmology
- Samoilenko Marina
Today, conjunctivitis is one of the most common eye diseases that affects both adults and children.
Therefore, the answer to the question is very relevant: how long does conjunctivitis last? The disease is not considered very serious, but despite this, it can lead to a large number of different problems and discomforts, so it is very important to know what the symptoms of such a pathology are and how to treat it correctly.
The disease begins suddenly and can disrupt all a person’s plans, which is why patients ask doctors this question: how long does conjunctivitis last? Please read the information provided carefully in order to arm yourself and protect yourself as much as possible. So let's get started.
What is conjunctivitis
The disease is an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the eye, which leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Please note that the causative agents of this disease can come both from the external environment and transfer from other foci of infections that already exist in the body.
Main forms of the disease
How long conjunctivitis lasts depends on many factors. The etiology of the origin of the disease should not be overlooked. There are several forms of conjunctivitis, namely:
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- allergic;
- viral;
- chlamydial
The bacterial variety of the disease occurs as a result of the active activity of pathogenic bacteria such as streptococci, gonococci, staphylococci and many others.
If we consider viral conjunctivitis, then the most common one is adenoviral infection, but in second place is herpetic infection. Typically, viral conjunctivitis does not occur as a separate pathology, but is an addition to other viral infections in the body. For example, most often it makes itself felt against the background of diseases such as measles or flu.
It is impossible to say unambiguously whether conjunctivitis is contagious or not, since in the presence of some forms of this disease you can still become infected, in particular through close contact, through your hands. Airborne transmission is unlikely. Therefore, regardless of how long conjunctivitis lasts, it is recommended to take a short sick leave. This is especially true if a child is sick.
Main symptoms of the disease
Before finding out how long conjunctivitis lasts in adults and children, you should first understand what the symptoms of this disease are. In fact, it is not difficult to recognize it, even by performing a visual inspection.
The first thing you should pay attention to is the mucous membrane of the eye. It turns red due to a significant increase in the size of the blood vessels.
It is because of this that people call this disease “pink eye disease.”
The patient usually complains of symptoms such as:
- unpleasant sensations in the eye, which can be described as itching and burning;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign object;
- excessive lacrimation, as well as fear of light;
- vision becomes less sharp;
- The visual organs get tired very quickly, even with the slightest load.
Of course, the child will not be able to clearly explain what symptoms are bothering him, so parents should pay attention to the condition of the baby’s eyes.
If the pathology is bacterial, its course may be accompanied by the presence of purulent discharge. With other forms of conjunctivitis, a large amount of mucous discharge will be observed.
Usually there are not very many of them during the daytime, but during the night they actively accumulate and can also dry out and stick the eyelashes together.
Sometimes there is so much discharge that the patient simply cannot open his eyes in the morning.
If the disease is of allergic origin, then there may be no excessive discharge at all, but the patient will be bothered by severe tearing, burning and light intolerance.
Many parents try to understand how long conjunctivitis lasts in children. In fact, it is impossible to give a definite answer, since the disease can have different origins and intensities.
Its most dangerous forms significantly worsen the patient’s general health, increasing body temperature and also leading to poor health.
Bacterial conjunctivitis: how long does it take to treat pathology caused by staphylococci?
If the inflammation in the eyes was caused by bacteria, then it is not recommended to take serious antibiotics. Ophthalmologists advise rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
However, if the disease has already become serious, then you still cannot do without antibiotics. Most often, bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by staphylococci.
In order to stop their reproduction, as well as relieve negative symptoms, you will need treatment lasting from five to seven days.
Pneumococci
There is no exact answer to the question of how long conjunctivitis lasts in children, since the disease can have different origins.
If the disease is caused by pneumococci, then all the symptoms of the pathology will be very pronounced, and the patient’s condition will be extremely serious.
Pneumococcal conjunctivitis is considered a disease of childhood, is quite contagious, and can be epidemic in children's groups.
Typically the course of treatment is about two weeks. At the same time, doctors strongly recommend taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory medications.
Gonococci
The most dangerous and serious form of conjunctivitis is considered to be a disease caused by gonococci. How many days does conjunctivitis last in this case? The course of treatment can take up to two months.
The infection process occurs through contact.
Adults can become infected through hygiene or household items, but such an infection can “catch on” to children during the birth process itself if the woman suffers from gonorrhea at the time of birth.
Please note that gonococci are very dangerous for children's eyes and can even lead to the child losing his sight completely. That is why, at the first symptoms of conjunctivitis, you should urgently contact a medical institution and under no circumstances self-medicate. Please note that it is very important to undergo treatment in a hospital, under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
Chlamydia
How many days does conjunctivitis in children caused by chlamydia last? According to doctors, it will take about fourteen to seventeen days to completely cure this type of disease. If there is a pathology, it is very important to make a correct diagnosis, because with incorrectly selected therapy you will greatly aggravate the existing problem.
It is very important to choose a local antibiotic that will be designed specifically to combat these bacteria. All other means will simply be ineffective.
It is best to use special drops during the daytime, and ointment at night, and apply it to both eyes at once, even if only one of them is affected.
How long does viral conjunctivitis last?
Most often, the viral form of the disease develops against the background of colds. If left untreated, it will be highly contagious. Infection can occur through household items, as well as aerogenously.
But how long the treatment will take depends on the patient. For some, five to seven days will be enough, and for others, even two months will not be enough. It all depends on the state of the immune system.
The illness is most difficult for children whose protective reactions have not yet fully formed. It is very important to carry out treatment with the help of antiviral drugs, as well as through the additional use of vitamins and immunomodulators.
In addition, it is also recommended to wash the eyes with herbal anti-inflammatory infusions.
Despite the fact that this form of the disease is considered relatively simple, it must be treated, as it can lead to significant deterioration of vision and even complete loss.
Allergic form of the disease
How long conjunctivitis lasts in a child depends on many factors, as well as the form of the disease.
Quite often, the disease can occur against the background of allergies, with both external and internal factors acting as irritants. It is possible that this pathology may occur due to the use of medications.
In this case, the disease affects two eyes at once. Its course is not very severe, but at the same time quite long.
Let's consider the features of treatment of this form of the disease:
- first of all, it is very important to exclude all contacts with the irritant;
- Doctors also recommend taking antihistamines and herbal medicines;
If the disease is severe, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids. However, they are prescribed only in cases where antihistamines have not had the desired effect. Typically the course of treatment is seven to fourteen days.
How to speed up the healing process
How many days does conjunctivitis last in a child is a question that worries many parents. It is impossible to answer it precisely, but general recommendations can be given that will speed up the recovery process.
Let's consider what causes the disease to never be completely cured or to return again after a short period of time:
- the patient suffers from a severely weakened immune system, especially for children;
- the patient was treated incorrectly, namely, did not follow the doctor’s recommendations or finished taking the prescribed medications ahead of schedule.
In such cases, the disease does not go away for up to several weeks or even months and can cause complete loss of ability to work. However, this can be avoided if you follow some recommendations, namely:
- At the first symptoms of the disease, immediately go to the hospital and do not self-medicate. You should not experiment even with proven home remedies.
- If possible, take sick leave during treatment and limit yourself from contact with other people.
- Please carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene. Wash your hands with soap and water as often as possible, and also use sanitizer. Change towels and bed linen regularly. If a child is sick, make sure that he does not rub his eyes with his hands.
- Avoid wearing contact lenses during therapy. Experts recommend purchasing new lenses after a complete cure and throwing away the old ones.
- During treatment, refrain from using decorative cosmetics.
Important nuance
Please note that if you use drops or ointment for five to six days and they do not help you, consult a doctor immediately. You will have to choose other medications. Today there are a huge number of them, so choosing the necessary effective remedy will not be difficult.
Final information
Many people think about the rules for treating eye conjunctivitis. How many days treatment lasts for children and adults depends on many factors.
You must understand that only you are responsible for your health, as well as the health of your child. Therefore, if you notice that something wrong is happening to your eyes, immediately go to an ophthalmologist.
The sooner you start the treatment process, the faster it will bear fruit.
Follow strictly all the doctor’s recommendations, do not self-medicate under any circumstances, and soon you will forget about what conjunctivitis is. Take care of yourself and be healthy. Do not forget that there are situations when vision cannot be restored.
Source: https://SamMedic.ru/431279a-skolko-dlitsya-konyyunktivit-u-detey-i-vzroslyih
How not to get infected?
It is better to prevent a disease in time than to treat it later. That is why the following preventive measures should be observed:
- Always wash your and your child's hands after going outside. Also, teach your child the importance of hand washing from infancy.
- Regularly strengthen your child's immunity. This can be either simple hardening or courses of additional vitamins (you should consult an immunologist about this).
- Explain to your child that you should not touch your eyes with dirty hands. In addition, you should not touch unfamiliar animals on the street.
- Isolate a sick child from a healthy one. If someone in the family gets conjunctivitis, so that others do not become infected, everyone should have individual towels.
- If your child is prone to allergies, be careful to isolate the allergen. During flowering, try to walk mainly in the evening, ventilate the room quickly and do wet cleaning of the room daily.
- When swimming in a pool, you should wear safety glasses to prevent water from getting into your eyes. Chlorine contained in water can cause allergic conjunctivitis.
- Never smoke in front of your child.
- In the summer, do not swim in places not intended for this.
It is almost impossible to protect yourself and your child from viral conjunctivitis. Outbreaks are especially common in kindergartens or schools, where children interact closely with each other.
If you are planning a pregnancy or are already expecting a baby, be sure to take all tests so as not to infect your child with gonococcal or chlamydial conjunctivitis during childbirth.
Useful video
All about conjunctivitis in the program Live Healthy!
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes - how long does conjunctivitis last in children and how to treat it
Any illness is always unpleasant, especially for a child.
In this article we want to talk about how long conjunctivitis lasts in children and how to treat it.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organs of vision, caused by tissue damage. protecting eyelids and eyes.
The causes of mucosal dysfunction are usually:
- contact with fungal or viral infections in the eyes (through the child’s blood or dirty hands with which he rubbed his eyes);
- allergies to seasonal flowers, dust or intolerance to any medications;
- chronic diseases of the organs of vision;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the child’s body.
Conjunctivitis is divided into three types:
- Viral.
- Bacterial.
- Allergic.
The duration of the disease depends on its type.
Symptoms of the pathology include:
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- burning and irritation in the eye area;
- after sleep, purulent or mucous discharge appears;
- the eyes get tired quickly and react negatively to bright lighting;
- active lacrimation.
Some types of inflammation are easily transmitted, so it is worth limiting the patient’s contact with healthy others to a minimum.
When bacteria is to blame
The duration of the disease is always affected by:
- a type of damaging bacteria;
- methods and methods of treatment;
- general state.
Staphylococcus, pneumococcus, gonococcus and chlamydia can get on the mucous membrane of the eye, which will become the impetus for the development of infection.
The most common case of infection is staphylococcus, but at the same time, the recovery process is also fast: up to 5 days.
This bacterium constantly lives on the mucous membrane of the eye, but has a chance to harm only those children whose immunity has weakened for some reason.
Washing the eyes with antiseptic solutions usually helps. It is extremely rare that antibiotics are used.
When affected by pneumococci, broad-spectrum antibiotics are added to the above therapy. However, recovery may take up to two weeks.
Gonococci are the most dangerous bacteria. They are usually transmitted to the newborn from a mother who has gonorrhea. There should be no self-medication here, only immediate consultation with a doctor! If you don’t delay your visit to the hospital, there will be no complications and everything will be forgotten like a bad dream.
An antibiotic will also help fight chlamydia. The duration of inflammation can reach 20 days, since first one eye is affected, and then the other.
We fight viruses
Viral dysfunction of the organs of vision usually affects children who have suffered from acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections or children with weakened immune systems.
This appears:
- cough;
- a sore throat;
- heat;
- swelling.
Viral conjunctivitis is not difficult to deal with. It is necessary to wash your eyes with disinfectant solutions, and every time after sleep, get rid of dried mucus or pus with a bandage moistened with tea leaves or infusions of chamomile, sage or calendula. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe antiviral ointments or drops.
You cannot let even the slightest inflammation take its course, so that the disease does not drag on and cause complications.
How long does allergic conjunctivitis last?
It is important to understand right away that the cause of this kind of inflammation can be chronic fatigue of the visual organs.
This disease is not transmitted, so others should not be afraid of it.
The main thing to do in such cases:
- try to achieve complete elimination of the allergen;
- reduce the load on the visual organs as much as possible.
If you cannot avoid contact with the allergen, you must be under the supervision of an ophthalmologist and strictly follow all his instructions.
For mild allergic dysfunction, lotions and rinses will suffice. In severe cases, there is no way to do without medications aimed at combating inflammation and allergies. Recovery comes in two weeks.
Many antiallergy medications are not suitable for children. Consultation with a doctor is required!
Babies under the age of one year should only instill eye drops with a pipette with a rounded end, so as not to damage the organ of vision itself.
Such children need to be laid on a flat surface, holding their head.
You need to pull back the lower eyelid and apply no more than 2 drops, which will distribute themselves over the eye, and remove the excess with a sterile bandage.
If an older child does not open his eyes, there is no need to be very worried or nervous. You just need to drop the prescribed medication between the eyelids, and when the child opens his eyes, the solution will still get on his mucous membrane.
Older children can be trusted to dribble their eyes on their own, but under adult supervision.
Cooled drops should not be used immediately; it is better to warm them in your palms so as not to aggravate irritation of the visual organs.
You should never use expired eye drops or purchase them from questionable places.
How to bring the moment of recovery closer?
Tips that you can follow to heal your child faster:
- Control the patient’s social circle until complete recovery, ideally to reduce those around him to zero (not counting those caring for the baby).
- Pay special attention to personal hygiene and treat your hands with antibacterial agents as often as possible.
- Reduce the time you use one towel and bedding, change it all more often than usual.
- Do not use any blindfolds.
- Monitor the cleanliness of toys.
- Do not forget about ventilating the room, keeping the air clean and humidified.
- Provide a balanced, fortified diet.
- Walk in the fresh air at least 2 hours a day.
- Do not forget about individual household items for the child.
- Do not attend a kindergarten or other educational institution, so as not to aggravate the course of the disease and not infect other kindergarteners or schoolchildren.
It happens that newborns show all the signs of mucosal inflammation, but even the most seemingly effective treatment does not help.
How can this be? Most likely, the diagnosis was incorrect and conjunctivitis was confused with another eye disease - congenital dacryocystitis (inflammation of the lacrimal sac).
This occurs in only 5% of babies, but this disease should not be discounted.
Its essence is that a film has formed in the nasolacrimal duct, which interferes with the outflow of tear fluid. Naturally, tears accumulate in the eye area, then “sour”, and all the symptoms of conjunctivitis appear.
How to distinguish between these two diseases? Here are the characteristic features of dacryocystitis:
- often only one eye is affected by inflammation;
- body temperature does not increase;
- Standard treatments for conjunctivitis do not help.
In most cases, the film in the nasolacrimal duct bursts on its own, so parents do not even know about its existence. If the film does not disappear on its own, then parents can wait up to a maximum of 8 months; after this point, they need to contact a specialist who will most likely prescribe probing (this is surgical removal of the film in the duct).
Does conjunctivitis affect vision?
In 90% of cases, conjunctivitis does not pose any particular danger to the child.
It often even goes away on its own, without drug intervention, only thanks to the active fight of the immune system.
No one dares to say that inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye cannot affect visual acuity.
There are such severe forms of this disease that can cause irreversible consequences. Therefore, for any dysfunction that lasts more than two days, you should definitely consult a specialist.
Source: https://momjournal.ru/zdorove-rebenka/detskie-bolezni/skolko-dlitsya-konyunktivit-u-detej.html