Signs of strabismus in children
In childhood, it is quite difficult to determine pathology if it does not manifest itself visually. This is due to the fact that the child cannot complain about the symptoms that bother him. There are signs that parents may suspect the condition:
- the child does not see surrounding objects well, so he begins to squint and ask his parents what is in the distance;
- if the strabismus is obvious, one or both eyes will shift from the straight axis while looking in front of you;
- Orientation in space is impaired, the child may constantly stumble or hit surrounding objects.
If parents recognize 1 of the above symptoms, they should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. The earlier therapy is carried out, the greater the possibility of complete restoration of the eyeballs.
Is strabismus inherited from parents?
Eye diseases can be transmitted from relatives
This article will help you understand whether strabismus is inherited. Many ophthalmological pathologies are determined at the genetic level. Whether a person wants it or not, they still make themselves felt sooner or later. We will figure out whether heterotropia is one of these disorders, and how to prevent its development.
Heredity and strabismus: are these concepts related?
A predisposition to certain disorders is inherent in a person at the genetic level. Ophthalmic diseases are no exception.
Genetics plays an important role in the formation of the optical system
The following can be transmitted from relatives:
Fact: The above diseases are included in the group of ametropic disorders of visual function.
Strabismus is a separate type of ophthalmological abnormality, which is associated with impaired binocularity and improper functioning of the eye muscles.
Opinion of ophthalmologists
Ophthalmologists are often asked the question of whether heterotropia is inherited from father, mother and grandmothers.
Ophthalmologists have not yet come to a consensus regarding this problem.
With strabismus, the muscles of the eye are not evenly developed
Important: Most experts are inclined to believe that strabismus is not inherited.
Doctors say that only a tendency to heterotropy can be transmitted at the genetic level. This is manifested in a certain structure of the eyeball and muscles.
When can hereditary heterotropia develop?
Hereditary strabismus occurs if:
- the baby was injured during childbirth;
- the child has suffered serious inflammatory diseases;
- the baby was diagnosed with congenital abnormalities in the central nervous system;
- other ophthalmological pathologies developed (hypertropia, myopia, astigmatism).
Damage to the brain during childbirth causes possible strabismus
Important: If you notice any signs of strabismus in your child or yourself, immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
How to prevent the development of a hereditary form of strabismus?
If one of the baby’s relatives has strabismus, then the parents are concerned about how to prevent heterotropia in infants.
To prevent the development of the disease, take preventive measures in time
- Do not hang bright toys close to the child's eyes.
- Do not bring any objects close to your baby's eyes, even if you are playing with him.
- Visit your ophthalmologist regularly for preventative purposes.
- Do eye exercises when your child reaches 6 months.
- Give your child a few squares of dark chocolate once a day, starting at age 3. Natural cocoa strengthens the eye muscles.
Dark chocolate is healthy and tasty
Compliance with preventive measures and regular visits to the ophthalmologist is the key to high visual acuity and “straight” vision!
Features of the development of strabismus
Strabismus is a pathological condition of the eyes, characterized by deviation of the pupils from the central axis.
People with heterotropia cannot focus their gaze on the object in question, as a result of which the visible image is distorted and doubled.
Strabismus refers to a pathology in which the patient lacks binocular vision, connecting the images of the retinas of both eyes into a single whole picture.
The brain excludes the information received by the squinting eye, and over time completely eliminates the participation of the affected organ of vision in the visual process. The reasons for the development of this condition can be very different - from fetal intoxication to head trauma. Under the influence of a number of factors, strabismus can develop at any age, but most often the disease is diagnosed in young children.
Forms of strabismus
Strabismus can occur in 2 forms:
- Friendly. Strabismus moves from one eye to the other, the deviation from the central axis in both organs of vision is almost the same. With concomitant strabismus, the movement of the pupils is preserved; when trying to focus the gaze, both eyes deviate. Most often it occurs in children and is inherited. Diplopia is not observed.
- Paralytic. Only one eye is squinting, the other is positioned correctly. The squinting eye is limited in movement towards the affected muscle. Paralytic strabismus is a consequence of paralysis of the extraocular muscles. A patient with this form complains of double vision, migraines, and dizziness.
Features of the development of strabismus in children
Many people consider strabismus to be a childhood disease. Heterotropia actually occurs most often in children aged 2-3 years. The following main reasons for the development of strabismus in a child can be identified:
- genetic disorders;
- fetal intoxication;
- birth injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- infectious pathologies;
- eye diseases;
- mental trauma.
Violation of eye position in childhood can be congenital or acquired. The congenital form of the pathology manifests itself in the first six months of life. Acquired strabismus usually develops before the age of 4 years.
Up to 6 months, the baby’s visual apparatus is still developing, so a slight deviation in the position of the eyes, not accompanied by oculomotor disturbances, is a normal condition (false strabismus), which goes away without medical help.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8qAjREeODc
The development of true strabismus in a small child will be indicated by the following symptoms:
- inability to concentrate both eyes on one point;
- noticeable deviation of the pupil to the side;
- non-synchronous eye movements;
- squinting of a squinting eye;
- constant bending and turning the head when trying to look at something.
Is strabismus inherited?
Many diseases can be inherited. Can strabismus be inherited? Experts' opinions on this issue vary. Many scientists are confident that if at least one of the parents or close relatives (grandparents, aunts, uncles) suffers from strabismus, then the child has a high probability of being born with such a pathology.
Types of strabismus
According to its forms, strabismus is divided into friendly and paralytic. Each of them has its own characteristics and subspecies.
The concomitant form of strabismus is inherited. With this pathology, each eye individually changes its trajectory. The eyes are active and can move around their orbits. The condition is divided into several categories:
- accommodative disorder - a different decrease in visual function by a large number of diopters for the right and left eyes separately, the violation of the angular position is the same for each organ;
- partial accommodative disorder - the motor ability of the eyeballs is partially limited, the difference between the diopters for the right and left organs of vision is small;
- not an accommodative disorder - the visual function for each eye is the same, but the angles of deviation between them are equal.
In the paralytic form, the muscles of the diseased eye can be completely atrophied. In this regard, it deviates greatly from the central trajectory. The second eye retains mobility and vision; it completely takes over all functions. Gradually, the brain stops sending signals to the diseased eye and uses the services of the healthy one. Therefore, patients lose binocular vision, it becomes monocular. This greatly reduces a person's quality of life. He begins to have difficulty oriented in space.
The paralytic form is divided into 3 categories.
- Vertical – the vertical muscle of the eye is weakened due to an imbalance in the development of the eyeballs and surrounding tissues. Another reason is the increased hardness of the vertical muscle, which begins to lose its elasticity.
- Converging. The reason for this condition is a decrease in visual acuity of the eye. A person may be farsighted or nearsighted. Due to the pathology, the eyes become very tired, which leads to muscle spasm. They begin to work incorrectly, the organ of vision deviates from its trajectory.
- Divergent. The cause of the pathology is a violation of intrauterine development. These may be diseases of the central nervous system, abnormalities in the structure of the eyeballs, differences in visual acuity of the right and left eyes. The central axis of the eyes moves greatly to the side.
The doctor needs to establish the formula of the disease in order to prescribe the correct treatment.
Can strabismus be inherited?
Skip to content
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers! Read more…
Is strabismus inherited? Strabismus (heterotropia) is a type of eye disease that causes the eyeballs to deviate from the central axis.
In this case, when looking forward, the position of one eye will be disrupted, and in some forms - two. In advanced forms of strabismus, severe loss of visual acuity is observed.
Acquired strabismus is not so severe, especially if strabismus is detected in a child in the early stages.
Forms of strabismus
Today, thanks to scientific research, only two forms of strabismus can be distinguished: friendly and paralytic.
Friendly form of strabismus
A form of strabismus, which includes a certain feature in the structure of the visual organs. In this case, the eyes may not squint symmetrically, but each on its own. The eyes are not limited in mobility. The disease is transmitted to the child in a hereditary manner. The friendly form is divided into three subspecies:
- Accommodative. It is characterized by pronounced ametropia (from 4 to 10 diopters) and equal values of deviation angles. An effective treatment method: optical correction.
- Partially accommodative. It is characterized by limitation in eye movement, and in some cases, absence of movement, in one or more directions.
- Non-accommodative. Characterized by the absence of ametropia. The deviation angles are the same. An effective treatment method: prismatic correction.
Paralytic form of strabismus
A form of strabismus, which is characterized by deviation from the standard trajectory (squinting) of the healthy eye.
This happens due to the fact that due to partial atrophy of the muscles of the diseased eye or its specific structure, the healthy eye is forced to take on the entire load when moving.
In this case, the healthy eye deviates to a greater angle. Acquired strabismus often has exactly this form.
Three types of strabismus are often observed in children:
- Vertical. It occurs due to an imbalance of the eye muscles, which in turn leads to a weakening of the vertical eye muscle. Another reason for this disease is abnormal seals on the vertical muscles, which leads to a deterioration in the elasticity of the corresponding muscle. The seal on the muscle can limit the vertical movement of the eyeball.
- Converging. The reasons for this form can be: heterophoria, farsightedness, hyperopia. Strabismus with converging strabismus is clearly expressed due to high fatigue and overexcitation of the eye muscles.
- Divergent (exotropia). This form in which the eyes have an external deviation. The reasons lie in intrauterine development: a strong difference in visual acuity, diseases of the central nervous system, congenital abnormalities in the structure of the eye.
Causes of strabismus in children
Unfortunately, strabismus is included in the list of diseases that are inherited. If the child’s parents suffer from strabismus, then in 90% of cases the child will be burdened with this disease.
It is also worth considering that if immediate relatives also suffer from strabismus, this increases the likelihood of transmitting the disease to the child. Therefore, when parents or relatives have strabismus, the child must be under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
With congenital strabismus, if the doctor identifies the disease in the early stages, this will make it possible to successfully treat it. In cases where strabismus is in an advanced form, its treatment cannot guarantee 100% effectiveness.
Therefore, if the question arises whether strabismus is inherited, you need to understand that in most cases it is transmitted.
The cause of strabismus in a child can be not only genetic abnormalities and heterotopia in the parents. Pathological processes during pregnancy, as well as during childbirth, can affect the development of strabismus in a newborn. The first reason is oxygen starvation of the fetus.
Due to hypoxia, the supply of the embryo with the required number of nerve cells is disrupted, which entails disturbances in the functioning of the eye muscles. The second reason is a spinal injury in the cervical region or, even worse, a brain injury.
Such injuries may result in innervation and repositioning of the visual muscles away from the visual axis.
We recommend!
To treat eyes without surgery, our readers successfully use a proven method. Having carefully studied it, we decided to offer it to your attention. Read more…
At an early age, the child’s body is especially sensitive and is exposed to external stimuli, which are more likely to affect further development:
- Head injury. Minor head injuries, which in turn can cause concussions, bruises or brain stress. Such a list has a fairly high probability of the child developing strabismus.
- Eye surgeries. If in childhood your child underwent eye surgery, such as laser coagulation, glaucoma, cataracts, etc., this may lead to postoperative complications, which in rare cases cause strabismus.
- Stress. If a child experiences severe stress or mental disorders at an early age, this can lead to impaired blood circulation in the capillaries and vessels, as well as overall pressure in the brain. Due to reduced pressure in the vessels of the eye muscles, the extraocular muscles may work abnormally. This, in turn, can lead to the development of strabismus.
But you should know that the eye muscles and nerve endings that envelop the eye develop on average up to 4 years. Therefore, hasty decisions in terms of operations may not always be correct. At what age can strabismus be detected?
Strabismus, like other types of eye diseases or abnormalities, begin to appear after the third year of a child’s life. This moment is due to the fact that the child actively begins to show interest in the world around him and his activity forces his vision, namely the eye muscles.
When a child begins to look at all sorts of small patterns, pictures, and engages in drawing and activities that increase the load on the gastric muscles, a deviation appears in the position of the visual axis. As a result of a violation of the axis, strabismus appears.
Strabismus can be detected even in the very first years of a child’s life if the strabismus is congenital and has a paralytic form.
Procedures for making an accurate diagnosis
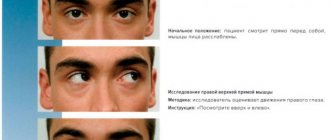
With congenital strabismus, an accurate diagnosis should be made immediately to the child. To do this, you will need to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist, which includes:
- Determination of visual acuity
- Checking the possibility of eye movement and the angle of deviation.
- Binocular vision test.
If a child suffers from strabismus, then in 99% of cases this is accompanied by diseases of the central nervous system (CNS). Children burdened with eye position disorders experience stress at an early age, as they have an insecure position in society, difficult relationships with peers, uncertainty, etc.
Treatment of strabismus
There are various methods for treating congenital strabismus in children. Doctors can always help you choose the most appropriate treatment method for your child after making an accurate diagnosis.
- Surgical intervention. The advantage of this method is that it is possible to eliminate the external sign of strabismus, but, unfortunately, it will not return visual acuity. The operation cannot completely eliminate the double image, since the brain, which has been accustomed to working in this mode for a long time, is responsible for the double image.
- Therapy. In this method, if the diagnosis is correct, the doctor prescribes the patient to wear glasses or contact lenses. The advantage of this method of treatment is that you can return your former visual acuity. The downside is that getting rid of the external aspect of strabismus will take longer.
By secret
- Incredible... You can cure your eyes without surgery!
- This time.
- No trips to the doctors!
- That's two.
- In less than a month!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
Heredity of strabismus
Strabismus is one of the diseases of the visual organs that can be inherited. This form of transmission does not always occur. The disease can appear due to mechanical damage, exposure to toxins, or decreased visual acuity in one eye.
If only one parent has strabismus, the chance of transmission is 50%. If the condition is developed in both parents, the risk increases significantly, amounting to at least 90%. The risk of the disease also increases if close relatives suffer from the pathology.
The pathological gene that determines strabismus may be located on the sex chromosome. If both parents suffer from strabismus and the child is given the chromosome responsible for this disease, it will develop in 100% of cases. If a pathological chromosome is passed on from the father, and a healthy one from the mother, the child may be born with healthy eyes.
If one of the child's parents suffers from strabismus, he may inherit a predisposition to developing this condition. So, if vision function decreases in only one eye, the disease will develop quickly.
Many people confuse hereditary strabismus with its congenital form. The second type can be formed as a result of a violation of intrauterine development. For example, if a small amount of oxygen or nutrients penetrated the placenta, the fetus had a spinal injury, and vision pathology in the form of strabismus may develop.
Strabismus and its inheritance: main signs
Strabismus means a deviation from the center of the axis of one or two pupils, while the eyes cannot look in one direction at the same time.
A common phenomenon in which one eye looks the way it should, and the other in the other direction. Or there is severe strabismus in both eyes. This disease is clearly visible to the naked eye.
It can be determined even without the help of a qualified specialist.
Strabismus is a disease that is visible to the naked eye.
It is enough to simply ask the child to look into his eyes. With such a visual experiment, you can see whether the eyes deviate from the desired position or not.
Quite rare, but still there is a hidden pathology that can only be identified by a specialist during examination. With strabismus, the child experiences disturbances in all eye contact.
Many people are concerned about the question: “Is strabismus inherited?”
Main signs of strabismus
The main signs of strabismus include the following symptoms:
- Inability to concentrate both eyes on one point. If the violations are not great, then they are not visible.
- The eyes do not move synchronously;
- If you look at a bright light, you can see that one eye moves to the side;
- In order to look at an object you need to turn and bend;
- When walking, the child collides with objects on the way without noticing them;
Older children complain of the following symptoms:
- Excessive eye fatigue;
- Visible objects are not clear;
- Sensitivity to light is pronounced;
- Seeing double.
If a newborn has a noticeable squint, the cause is usually muscle weakness. By six months, the muscles become stronger and the eyes take the correct position.
Strabismus in children, its forms and causes
Many parents do not pay much attention to this pathology, as they believe that it is just a cosmetic defect. But this is not true at all. Strabismus is a serious pathology that requires examination by a specialist and treatment. After all, sometimes the transmitted volume of visual information is not complete and in insufficient volume, due to the development of pathology.
The disease develops when children reach 2 or 3 years of age. It is at this time that the child develops coordinated work of both eyes. Thanks to statistical studies, every 55th child has these deviations.
There are many reasons for this disease. To identify problems, you need to sort it out together with your doctor. A common cause is the development of strabismus due to weakness and overtraining of the muscles. Also in the presence of myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism. The child strains his eyes very much when looking at an object, and this leads to the fact that his eyes begin to squint.
The cause of strabismus from birth is certain types of illness suffered by the mother during pregnancy. If any eye abnormalities are noticeable, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to diagnose and establish the cause, type and degree of pathology, and also prescribe the necessary treatment.
Only a doctor can diagnose the type and degree of pathology
Ophthalmologists have several classifications, the most commonly used is the one that has three types.
The main types of strabismus in children:
- Imaginary strabismus. Occurs mainly in infants. Due to the anatomical structure of the eye, it often appears that the eyes are squinting. There is no reason to worry, since with age the child’s defect disappears completely. If the specialist has rendered a verdict - imaginary strabismus, then the parents should be calm and after a while there will be no trace of strabismus left.
- Esotropia is characterized by deviation of the pupil towards the nose. In turn, it is divided into:
- Congenital, which occurs due to a predisposition to this disease. Occurs in children in the first six months of life. When tired, the eyes begin to squint even more.
- Accommodative. Children from 9 months to 4 years are most susceptible to this type. The cause is farsightedness. If objects are at a close distance, then the child, when concentrating his gaze, strains his vision very much and after a while, pathology develops.
- Exotropia. With this strabismus, the eye deviates towards the temple. It is detected in children older than 1 year. When looking into the distance, a deviation becomes noticeable. The child may complain of headache, double vision, and so on.
Is strabismus inherited?
A sufficient number of diseases are inherited, and this pathology, alas, is no exception.
If the mother, father, or immediate relatives suffer from strabismus or some eye diseases, then there is a high probability that such a disease can be passed on to the child.
Therefore, if there is a possibility of transmission of this disease, the child should be observed by an ophthalmologist in order to identify the disease in the early stages. After all, if strabismus is in the initial stages, it is easier to cure than in advanced stages.
Strabismus is one of the diseases that is also inherited
If the correct position of the visual axes is disturbed, then strabismus is immediately visible. In medical practice, there are cases in which children develop the disease in a latent form. There are no signs that it exists and it occurs when there is a muscle imbalance. The eyes are able to move thanks to 6 muscles that have different tensions.
If something goes wrong in the tension, muscle imbalance occurs. According to statistics, 80% of the population suffers from this disease. There is no discomfort, but it can lead to myopia in the future. Every parent wants only happiness for their child, and hereditary diseases are a big blow, both for the child and for the father and mother.
Development of strabismus and procedures necessary to make a diagnosis
As a rule, strabismus is detected during a routine examination of the child. An ophthalmologist checks your vision using instruments and a computer, and also suggests taking several tests. After this, the doctor can tell you about the condition and presence of pathologies in the child.
From two to three years old, the child begins to show interest in activities that require focusing attention and straining his eyesight.
These include modeling, drawing, looking at pictures, puzzles, inserts, and so on. At this age, the eye muscles are not yet so strong, and due to increased stress, strabismus may develop.
Or the reason is at the genetic level, then external factors will not affect it in any way.
At the first symptoms, consult a doctor
If there are any signs, you should immediately consult a specialist, namely an ophthalmologist. It is the doctor who will prescribe a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- Initial vision test;
- Determination of eye position and angle of deviation, if any;
- With wide and narrow pupils, refraction is determined;
- Binocular vision testing.
As a rule, those children who have strabismus suffer from certain abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system. This includes neuroses, as well as problems associated with this disease. Therefore, if a pathology is detected, it is necessary to immediately consult a neurologist.
If the identified strabismus is not treated, then for the child it will be a major defect in appearance, which can lead to the development of an inferiority complex. Over time, the visibility of the diseased eye will only worsen.
Necessary treatment
As soon as the diagnosis of strabismus is made, you can immediately proceed to treatment, without delaying or expecting it to go away on its own. Treatment requires compliance with all points of the recommendations, as well as constant medical supervision. Regardless of whether strabismus is congenital or acquired, it must be treated.
The first thing you need to do is cope with myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism. From a very early age, the child begins to wear glasses. They must be worn constantly and for a long time. It is very important during this period to perform the necessary set of exercises that should create visual stress.
If you have strabismus, you must first deal with myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism.
If some complications suddenly develop, it is recommended to wear glasses with one eye taped. This increases the load on the sore eye, thereby training the muscles.
If all these methods do not bring the desired result, the patient is referred for surgery. During the procedure, the eye muscle is either made shorter or moved to a different location altogether. As a rule, there are no contraindications for performing it between the ages of three and six years.
For small children, the operation is performed using general anesthesia, since it is not so easy to restrain a small child during the procedure, and any careless movement of the doctor is fraught with consequences. For older children, local anesthesia is recommended, in which painkillers are injected into the area around the eye. The recovery period is 10 days.
After recovery, it is also necessary to carry out exercises and be constantly monitored by an ophthalmologist.
Measures to prevent strabismus
The most common of all existing eye pathologies is strabismus. And, as a rule, this process is reversible, so it is necessary, first of all, to pay great attention to preventive measures.
If a child has strabismus, he needs the love and support of his parents first of all.
At the first examination, the ophthalmologist can give a realistic prognosis and if you need to immediately correct your vision with glasses. If you start preventive therapy after one year, it is possible to halve the disease of strabismus in children. This requires coordinated action between doctors, parents and the child; only in this case are positive results possible.
We can draw the following conclusions: by strictly following all the ophthalmologist’s recommendations, it is possible to achieve tangible positive results. Children who have strabismus have decreased self-esteem and have complexes about their appearance. The child becomes irritable and withdrawn.
If a child is laughed at at school, and this is due to his illness, then parents first of all need to support the child. In this situation, all measures are good, both father's advice and mother's love. Be healthy you and your children.
Dec 24, 2016Doc
Treatment
The method of therapy depends on the severity and form of the disease. An integrated approach is required to eliminate the condition, as well as the risk of relapse:
- Restoring vision in case of myopia or hypermetropia. The patient may have reduced function of only one organ of vision, as a result of which strabismus develops. Such patients need to wear an adhesive or fabric bandage on the healthy eye so that the second organ of vision gradually begins to work.
- Hardware treatment. Devices are used that provide images to both eyes. While watching them, training of the muscles of the sore eye begins. Subsequently, it begins to function in the same way as a healthy organ of vision.
- Surgery. The doctor corrects the function of the extraocular muscles by cutting the extraocular muscle and then suturing it with the necessary tension. Thus, the patient's eyes are established in a normal location, long-term therapy is not needed. But if the primary factor is not eliminated, the condition may reoccur.
It is recommended to begin therapy immediately after identifying the condition. The sooner it starts, the higher the possibility of a complete cure.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
This type should not be confused with myopia, caused by increased tone of the muscles involved in accommodation (false myopia). Let's consider true refractive myopia.
Changes in eye structures leading to the development of myopia:
- an enlarged eyeball is the most common pathology;
- keratoconus (deformed cornea);
- violation of the correct position of the lens due to injury;
- sclerotic changes in the lens in the elderly.
The first symptoms of the disease most often appear at school age, but the disease can also be diagnosed in very young children. What are the reasons for such an early development of the disease?
From the above, it became clear that the leading factor in the development of the disease is a change in the normal shape of the eyeball, namely: its elongation. It is currently believed that the main reason for the development of myopia is heredity. The disease is transmitted to the child from parents through genes.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing strabismus or recurrence of the condition after treatment, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- annual examination by an ophthalmologist, as well as prescribed treatment;
- wearing corrective lenses or glasses if vision is reduced, especially in one eye;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, as they can lead to decreased vision function, for example, hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease;
- During pregnancy, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle, take vitamins, and not be exposed to stress, as all these conditions increase the risk of abnormal fetal formation.
Strabismus is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a disease that can lead to a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. It must be treated promptly. This is possible only after establishing the root cause of the disease, one of which is heredity.
Causes of why strabismus may develop
Causes of strabismus:
- Congenital defects of the visual apparatus.
- Injuries and paralysis.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Psychosomatic disorders.
- Concomitant diseases of the visual department.
- Abnormalities or weakening of the visual muscles.
- Side effects of drugs.
The appearance of strabismus can be preceded by stress and psycho-emotional stress. In young children, this disease can develop even under the influence of severe fright, and in adults, the most common cause is injury or exacerbation of other diseases.
Strabismus can be a consequence of a heart attack or stroke, and in some cases even infectious diseases.
This leads to accompanying vision problems: myopia (farsightedness) or astigmatism develops. With age, the risk of such a disease only increases, so you should not neglect routine eye examinations by a specialist.
On video: what is strabismus, the causes of its occurrence in adults and treatment
Kinds
Like any disease, strabismus is characterized by various types of its manifestation.
If strabismus is suspected, the ophthalmologist may prescribe additional examinations, but usually such symptoms are visible to a specialist during a personal examination of the patient.
Friendly
Deviations from the central axis of both eyes are approximately the same, and such a symptom signals other vision problems. Most often, concomitant strabismus develops with simultaneous farsightedness or ametropia (a change in the refractive power of the human eye for perception).
Divergent
This type of disease most often affects people with myopia, or is a consequence of such a deviation. In this case, the eyes diverge towards the temples, focusing is also difficult. In children, divergent strabismus is very common, but is easier to correct.
Convergent
In this case, the focus of the eyes is shifted to the bridge of the nose. Convergent strabismus also occurs with a simultaneous decline in visual function. Converging occurs most often in childhood, and in some cases it stabilizes on its own.
Vertical
Vertical strabismus is a fairly rare disease in which the eye (or both eyes) involuntarily shifts up and down.
Paralytic
Paralytic is diagnosed when one or both eyes are permanently displaced. In fact, the visual function in this case is practically blocked. Among the most common causes are previous injuries and diseases, as well as atrophy of the visual muscles. Paralysis can occur at any age, but most often affects older people.
Atypical
Manifests itself under the influence of concomitant developmental anomalies. Most often these are chromosomal abnormalities and anatomical features of the structure of the visual center. Read this material on how to use the Synoptophore device at home.
According to the degree of manifestation, strabismus can be constant or periodic.
The problem worsens under the influence of external unfavorable factors, for example, fear or excitement.
Related Oncology
Cancer problems are often hereditary, especially tumors in the breast, ovaries or intestines. According to doctors, if there was one carrier of the pathology in the family, you should be wary, but if there are two of them, you should definitely get examined! In addition, it is necessary to take into account the age at which the parents developed the problem. For example, the likelihood of a daughter developing tumors increases if the mother’s problems were discovered before menopause - in this case, it is most likely due to gene mutation. Why is it easier for several family members to get a similar pathology at once? In a genus, a set of genes that is approximately identical in structure with minor differences is inherited. This means that the problem can easily arise in the same areas.
There is only one way out in this situation - timely and regularly consult doctors and get tested. Thus, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist, endocrinologist, oncologist-mammologist and proctologist.
Article on the topic
We treat genes. How to overcome bad heredity?