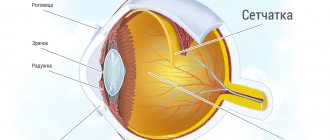
What is retinal tomography?
Computed tomography of the retina (also known as optical coherence tomography) is popular and trustworthy among ophthalmologists. As you know, medicine does not stand still, and these days we have the opportunity to undergo a retinal examination using such a non-contact and painless method as computed tomography.
A tomograph uses X-rays to scan the top of the patient's head. Ultimately, the specialist displays images of the eye sockets layer by layer on the screen, which allows him to assess the condition of the retina and optic nerve, identify the initial stages of diseases, and therefore prescribe timely treatment to the patient.
Angiotomography of the eye
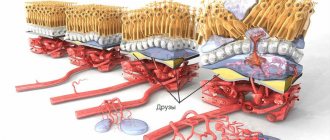
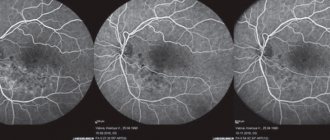
Optical coherence tomography with the function of angiography of retinal vessels (angioOCT/angioOCT, OCT with angiography/OCT with angiography) is an innovative non-invasive method for studying the vessels of the central zone of the fundus of the eye - the retina and choroid, which also allows assessing the state of the vascular network of the Optic Nerve Disc (OND). ).
The OCT angiography (OCTA) method is based on recording the movement of blood through the retinal vessels (retinal vessels) and choroidal vessels, which allows in high resolution to obtain a complete picture of the small vessels of the fundus and to see hidden vascular pathology that is inaccessible to detection by other methods.
The uniqueness of the method is that the study is carried out without the use of intravenous dyes and is absolutely safe. Visualization of blood circulation without the use of a contrast agent eliminates a number of risks, for example, allergic reactions to it and other complications. Moreover, in most cases, OCT does not even require pupil dilation with special drops. The absence of the need for special preparation is extremely convenient for patients, and in addition significantly reduces the examination time!
The new diagnostic method is absolutely painless.
The study does not require much time; about 30 seconds are enough to obtain detailed data about the vascular system of the retina and optic nerve.
The subject does not get tired during the study, which is very important for elderly patients.
The complete absence of blinding photo flashes during the examination makes angiotomography comfortable.
How is the research going?
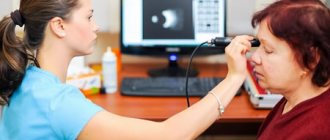
The examination is carried out in a sitting position behind the device, the chin is placed on a special support (facial installation). The patient is required to look in the direction of the test mark for several seconds.
When and what is it used for?
Computed tomography with eye angiography function is performed for many diseases of the fundus and optic disc:
1. Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
2. Myopic maculopathy
3. Chorioretinitis
4. Hereditary retinal diseases
5. Occlusion of retinal arteries and veins
6. Specific retinopathy in various general diseases, incl. diabetic retinopathy
7. Glaucoma
8. Anomalies in the development of the optic disc and its atrophy.
AngioOCT makes it possible to identify dangerous diseases of the fundus of the eye at the earliest stages, which in turn makes it possible to prescribe timely and therefore effective treatment at the earliest possible date.
Angiotomography for glaucoma
Thanks to the development of technology, perimetry and tonometry data are no longer the only grounds for making this diagnosis; optical coherence tomography and angiotomography are actively used.
AngioOCT significantly helps in the early diagnosis of glaucoma and in monitoring this terrible disease. OCT angiography visualizes all layers of the optic disc and retinal nerve fibers, allowing you to evaluate the exact areas and layers of the lesion when the patient does not yet complain about a decrease or loss of visual fields.
AngioOCT in cases of retinopathy
Using angioOCT for postthrombatic retinopathy, the presence of foci of ischemia in the central zone of the retina (areas with impaired blood flow) is detected. And thanks to timely laser treatment of these areas that do not receive nutrition, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of complications, for example, secondary glaucoma (which, without timely treatment, often ends in complete and irreversible blindness).
AngioOCT demonstrates all changes in retinal vessels in such a severe chronic disease as diabetes mellitus. It allows layer-by-layer visualization of the vascular network of the eye in frontal and transverse sections from the superficial to deep layers, as well as the outer retina and choriocapillaris.
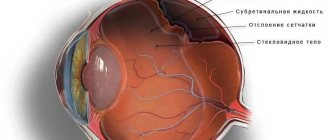
Diabetic retinopathy (an eye disease that is a complication of diabetes mellitus) is characterized by pathological vascular permeability, swelling and hemorrhages in the eye cavity (hemophthalmos), rupture and detachment of the retina. Angiotomography allows you to detect the slightest hemorrhages: microaneurysms, hemophthalmos, the growth of new pathological vessels. Timely comprehensive ophthalmic treatment in these cases gives hope for the preservation of vision!
OCT angiography for AMD
In the case of the “dry” form of AMD, the angiotomogram visualizes a decrease in blood flow in the macular (central) zone of the retina. The assistance that angioOCT provides to the ophthalmologist in quantifying blood flow is invaluable!
In the “wet” form of this disease, OCT angiography provides the opportunity to assess the density, shape, branching and volume of the capillary network vessels, as well as to observe the dynamics of the area of the network of newly formed vessels against the background of anti-VEGF therapy and see the effect of the treatment.
In the clinic, angioOCT is performed by highly qualified retinologists (retina specialists) with many years of experience and on a new tomograph SOCT REVO, Optopol (Poland) with an angiography module with amazing image quality, which guarantees accurate diagnosis and the effectiveness of further treatment.
AngioOCT is a modern, highly informative diagnostic study, with the help of which it has become possible for ophthalmologists to diagnose eye diseases at a completely different level of technological development.
When is optical coherence tomography of the eye prescribed?
Indications for the procedure
Optical coherence tomography of the eye is a common diagnostic method, so ophthalmologists quite often resort to this procedure. The main indications for this study are the following:
- presence of foreign bodies or suspicion of them;
- sharp decrease in vision;
- pain in the eyes;
- tumors of the walls of the orbits (benign or malignant);
- injuries to the eye sockets or orbits;
- protrusion of the eyeball (in medical terms, exophthalmos);
- inflammatory processes;
- lesions of the lacrimal glands caused by autoimmune diseases.
Advantages of coherence tomography
This is one of the best methods for diagnosing glaucoma, which completely determines the cause of the development of pathology and changes over time. The technology has also proven itself to be excellent for determining macular degeneration, which is characterized as the formation of a black spot in the tissues of the eye.
Despite the high accuracy of the OCT method, specialists often prescribe it in combination with fluorescein angiography of the retina. The combination of two technologies allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and select the right treatment strategy.
How to prepare?
Similar to computed tomography of other human organs, examination of the retina can be performed using contrast (iodine-containing substance), so the patient should refrain from eating 4 hours before the scheduled time of the procedure. No other preparatory measures (for example, tests, ultrasound) are required for a CT scan of the retina. Immediately before starting the tomography, the patient should remove all metal objects and jewelry, as they can greatly distort the results of the study due to the specific design of the computed tomograph. It is necessary to warn your doctor about possible allergic reactions to the dye.
Biomicroscopy
This diagnostic method is also called ophthalmoscopy using a slit lamp. With its help, it is possible to examine in detail all areas of the fundus. Contact and non-contact lenses with different optical powers are used in the examination. They allow you to study the state of the internal structures of the fundus as accurately as possible.
Non-contact binocular ophthalmoscopy - examination using an aspheric lens equipped with strong diopters (+60.00, +90.00, +78.00D). It provides a clear reverse image of the fundus with a field of view of 70-90 degrees. The distance between the patient's cornea and the binocular non-contact ophthalmoscope is only 1.5-3 cm. The device is located perpendicular to the eye. The slit lamp is retracted to the maximum distance, after which it is slowly brought closer to the subject. The doctor examines the center and peripheral part of the fundus of the eye in a wide view, and the device does not come into contact with the patient’s eye.
Contact binocular ophthalmoscopy using a slit lamp and contact optics requires instillation of anesthetic drops into the patient's eyes. After their instillation, a disposable contact lens (diagnostic) is installed on the cornea. The patient places his chin on the rest, pressing his forehead against the bar of the slit lamp. You need to look straight ahead. After this, an examination of the fundus begins. A variety of types of ophthalmoscopes with different numbers of lenses and mirrors can be used. The width of the view depends on their number. Using non-contact binocular ophthalmoscopy, the doctor can obtain a high-quality image in which all parts of the retina will be visible.
How is the procedure done?
As mentioned earlier, the procedure for computed tomography of the retina takes no more than one minute (without the use of contrast) and about 15 minutes if an iodine-containing substance is required (in which case it is performed on an empty stomach). Before starting the diagnosis, the doctor talks about how the whole process will go. It is worth noting that patients have no reason to worry - the study is not only short-term, but also painless. The examination process itself is as follows: after the patient has removed all metal objects, he is asked to lie down on a special table, which will subsequently be advanced into the tomograph so that the patient’s head falls into the scanning area. As with other types of tomography, the patient must remain motionless.
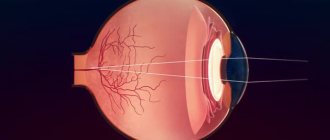
3D visualization
A black-and-white three-dimensional image is displayed on the radiologist’s computer, which allows you to examine the eyeballs, retina, and optic nerve from all sides. The image can be enlarged to view fine details. All results are saved on the computer of the clinic where the retinal CT scan is performed.
Advantages of the method
First, the main advantage of retinal computed tomography
is non-contact, since the eyes are highly sensitive to any touch and interference. Secondly, the procedure takes no more than a minute (provided that no contrast is used). Thirdly, the diagnosis is absolutely painless (due to the fact that there is no physical intervention). Retinal OCT allows doctors to obtain detailed and clear information about the patient's eye condition, which is a definite advantage. Finally, this diagnostic method is quite inexpensive, its cost can reach 3000-4500 rubles.
When is ophthalmoscopy prescribed?
This research method is the most common in ophthalmology. It is carried out using an ophthalmoscope - a special device that allows you to examine in detail the internal structures of the eye: the retina, vitreous body, optic disc, blood vessels, as well as the peripheral parts of the eyeball. Thanks to ophthalmoscopy, it is possible to identify severe pathologies of the visual organs at the very beginning of development. Among them:
- cataract;
- neoplasms;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- retinal detachment;
- glaucoma;
- macular degeneration;
- melanoma;
- cytomegalovirus retinitis;
- pathology of the blood vessels of the eyes.
Moreover, during an examination with an ophthalmoscope, not only ophthalmological diseases can be detected, but also diseases of a systemic nature, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, renal failure, and tuberculosis.
Ophthalmoscopy is prescribed for every visual examination. It can be considered a standard procedure that is included in any examination by an ophthalmologist. A referral for an ophthalmoscopy can be given not only by an ophthalmologist, but also by a cardiologist, infectious diseases specialist, gynecologist, and therapist. This diagnostic method is very important for pregnant women. During pregnancy, patients with myopia have an increased risk of retinal detachment. With the help of an ophthalmoscope, this dangerous disease can be detected at a very early stage and laser coagulation can be prescribed.
The following diseases and symptoms may also be indications for ophthalmoscopy:
- color blindness;
- eyeball injuries;
- myopia;
- inflammatory processes in the eye;
- traumatic brain injury;
- headache;
- epilepsy;
- violation of movement coordination.
There are also a number of limitations to the purpose of this research method. It is not performed in case of increased photosensitivity, lacrimation, clouding of the optical media of the eye, miosis and other pathologies of the pupils. Under these conditions, it will be impossible to examine the fundus in detail. In addition, symptoms such as tearing and photophobia may increase. Ophthalmoscopy is not always prescribed for angle-closure glaucoma. There is a risk of increased intraocular pressure. The method is not used in the presence of cardiovascular diseases. Contraindications may include various infectious and inflammatory diseases of the anterior parts of the eye.
Contraindications for CT scanning of the retina
Like many other types of examinations, retinal CT has contraindications:
- since during this procedure the body receives a certain dose of radiation, which can negatively affect the development of the fetus, diagnostics are contraindicated during pregnancy;
- age up to 14 years;
- allergic reactions to the dye;
- renal failure (contrast is excreted from the body thanks to the kidneys, therefore, can negatively affect their condition);
For those suffering from claustrophobia, there is no reason to be concerned, since only the patient's head is in the scanning area.
Interpretation of eye tomography results
The tomography results are not only a three-dimensional image and layered images, but also various tables, diagrams and protocols. To decipher the results obtained, a specialist can use an additional database stored in the tomograph’s memory. As a result, the doctor receives data on the characteristics of tissues, the localization of thickening and thinning, the location of damage and pathologies, their size, and degree of development. In other words, all the necessary parameters to make a correct diagnosis.