© Author: Z. Nelly Vladimirovna, doctor of the first qualification category, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Ocular pressure, intraocular pressure (IOP) or ophthalmotonus, is the pressure of the fluid contained inside the eyeball on the walls of the eye. Intraocular pressure is now determined for all persons who have crossed the 40-year mark, regardless of whether the person makes complaints or not. This is due to the fact that increased eye pressure is the main prerequisite for the development of a disease such as glaucoma, which, if left untreated, leads to complete blindness.
Intraocular pressure is measured using a special tonometer, and the results are expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). True, ophthalmologists of the 19th century judged the hardness of the eyeball by pressing on the eye with their fingers. In other cases, in the absence of equipment, a similar method is used today as a preliminary assessment of the condition of the visual organs.
About the norm of IOP in women
Normally, ophthalmotonus in the fairer sex varies between 10-23 mm Hg. Art., under such conditions, microcirculation/metabolic processes proceed unhindered in the membrane of the eye. This pressure indicates the normal functioning of the visual organs, when optical functions are completely preserved.
Eye pressure in women
If you do nothing, your vision may quickly deteriorate, and your eyes will begin to get tired when watching movies, reading books, or working at the computer. All these signs are a good enough reason to visit a doctor as soon as possible, since they can lead to the development of glaucoma in the future. Typically, such a deviation is observed mainly in people after 40 years of age.
If IOP is reduced, the patient is diagnosed with ocular hypotension. This phenomenon can be caused by the following provoking factors:
- surgery;
- eye infection;
- injury;
- decreased blood pressure;
- dehydration, etc.
Normal eye pressure in adults, table
Exactly what normal pressure should be depends largely on the measurement method used: each method has its own scale, and therefore there is no point in comparing the results. When choosing a specific method, it is necessary to take into account, first of all, the patient’s condition. As mentioned earlier, according to Maklakov, the IOP norm is approximately 10-23 mm Hg. Art.
Man at an appointment with an ophthalmologist
Any deviations in this case indicate an uneven distribution of nutrients throughout the tissues of the eye.
And if you don’t pay attention to this in time, you can ultimately lose your vision completely. But in some cases, the patient does not feel discomfort even when eye pressure goes beyond normal limits
Causes of high eye pressure
Table. Possible causes of IOP deviation.
| Name | Short description |
| Various types of disruptions in the body | These disruptions can activate the secretion of natural fluid in the visual organs |
| Anatomical changes | People who suffer from farsightedness or atherosclerosis need to closely monitor their eye health; the same applies to those whose relatives suffer from these diseases |
| Problems in the cardiovascular system | They often lead to increased pressure – both arterial and intraocular |
| Various complications | We are talking about any complications after previously experienced serious illnesses |
| Stress and strain | Stressful situations, as well as strong mental/physical stress, can cause IOP deviations from the norm. |
Stress can cause eye pressure to deviate from normal
- prolonged or increased strain on the eyes (reading, working at the computer, watching TV);
- predisposition to pathology by inheritance;
- eye diseases, including infectious ones;
- tumor formations in the eye area (of any nature);
- ingestion of toxic chemicals into the body;
- hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause, menstruation);
- living in a poor ecological area;
- negative reaction to eye medications or violation of instructions for their use;
- eye injury;
- complication from eye surgery;
- frequent stress or nervous strain;
- age and gender. Women and older people are more likely to experience changes in intraocular pressure;
- anomalies during intrauterine development;
- violation of the removal of fluid from tissues (expressed by the development of swelling) or dehydration of the body (poisoning, lack of fluid intake);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (vascular disorders, high/low blood pressure, heart failure).
Poor diet, alcohol/nicotine consumption, lack of sleep also affect IOP.
Why is it important to know IOP?
The attention paid to such an indicator of health status as intraocular pressure is due to the role played by IOP:
- Maintains the spherical shape of the eyeball;
- Creates favorable conditions for preserving the anatomical structure of the eye and its structures;
- Maintains blood circulation in the microvasculature and metabolic processes in the tissues of the eyeball at a normal level.
The statistical norm of eye pressure, measured by tonometric method, is within 10 mmHg. Art. (lower limit) – 21 mm Hg. Art. (upper limit) and has average values in adults and children of the order of 15 - 16 mm Hg. Art., although after 60 years there is a slight increase in IOP due to the aging of the body, and the norm of eye pressure for such persons is set differently - up to 26 mm Hg. Art. (tonometry according to Maklakov). It should be noted that IOP is not particularly constant and changes its values (by 3-5 mm Hg) depending on the time of day.
It would seem that at night, when the eyes are resting, eye pressure should decrease, but this does not happen in all people, despite the fact that the secretion of aqueous humor slows down at night. Closer to the morning, eye pressure begins to increase and reaches its maximum, while in the evening, it, on the contrary, decreases, therefore, in healthy adults, the highest IOP values are observed early in the morning, and the lowest in the evening. Fluctuations in ophthalmotonus in glaucoma are more significant and amount to 6 or more mm Hg. Art.
Treatment of high eye pressure
Today, the most common and accessible way to reduce increased ophthalmotonus is the use of special drops that normalize it. But it is also necessary to take into account the reasons that provoked the increase in IOP, and, if possible, eliminate or treat them. In addition to drops, there are also several other methods of combating high eye pressure. An ophthalmologist can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures (vacuum massage, color pulse therapy, etc.), which are carried out in a hospital setting.
The most drastic way to normalize blood pressure is surgery. There are also several types of them: goniotomy, trabeculectomy and the most advanced method - laser surgery. With the help of a laser beam, the outflow pathways of intraocular fluid are opened, as a result of which the ophthalmotonus decreases. But, unfortunately, in order to undergo the operation, the patient must meet certain requirements, and not everyone fits them. In any case, the treatment method is selected individually depending on age, severity of the disease, and individual characteristics of the body.
How to lower eye pressure at home
How to relieve eye pressure at home without resorting to medications? If the pathology has just begun to manifest itself, then by taking simple preventive measures, you can eliminate the risk of complications. To do this, you need to avoid wearing clothes that block the flow of blood from the veins of the head (do not wear ties, do not wear tight collars). In addition to restrictions on physical and mental activity, you can lower eye pressure at home in the following ways:
- do not tilt your body down;
- give up alcohol and cigarettes;
- exclude coffee, tea, salt;
- do not drink a lot of liquid;
- light massage on the upper eyelids.
How is eye pressure measured?
At home, the patient can use only one method available to him - palpating the eyeball through the eyelids, determining by touch the degree of its density. If the pressure is normal, then with gentle pressure you should feel a moderately elastic round ball under your fingers. With an increased IOP, it will be quite hard and not prone to deformation, but with a decreased IOP, on the contrary, it will sag. Of course, this method does not give correct readings and can only be used to understand the approximate condition, although people suffering from elevated IOP acquire the necessary skills over time. The exact data can be found in the doctor’s office, where he will conduct an examination using special instruments and also examine your fundus.
Tonometric measurement method. This is done using a tonometer. There are several types of them, but the most famous and common are Maklakov tonometer and Goldman tonometer
We will not go into technical details and a description of the measurement procedure, the only important thing is that these methods will help determine the exact intraocular pressure. Non-contact tonometers. Sophisticated electronic devices that are increasingly used today, as this method gives even more accurate readings
If, with the help of the first two tonometers, a direct effect is made on the eye, drugs are used to anesthetize the cornea, since there is a physical effect on the organ of vision, then with the help of a non-contact tonometer, measurements are carried out using a stream of air directed at the cornea.
Decreased fundus pressure
Doctors involved in the treatment of eye diseases are also aware of another phenomenon that is opposite to increased IOP - ocular hypotension, eye hypotension or decreased fundus pressure. This pathology develops quite rarely, but this does not make it any less dangerous. Unfortunately, patients with eye hypotony reach the ophthalmologist's office when a significant percentage of their vision has already been lost.
This late presentation is explained by the fact that there are no obvious signs of the disease; the initial stage proceeds almost without symptoms, except for a not very pronounced decrease in visual acuity, which people attribute to eye strain or age-related changes. The only symptom that appears later and can already alert the patient is dry eyes and loss of natural shine in them.
Factors that contribute to a decrease in intraocular pressure are not as diverse as the prerequisites that increase it. These include:
- Injury to the organs of vision in the past;
- Purulent infections;
- Diabetes;
- Dehydration
- Arterial hypotension;
- Alcoholic drinks and drugs (marijuana);
- Glycerin (if consumed orally).
Meanwhile, a person who pays as much attention to the eyes as other organs can prevent the unwanted effects of lowering IOP by visiting an ophthalmologist and talking about the above-mentioned “minor” symptoms. But if you do not notice the signs of eye health in a timely manner, you may find yourself faced with the development of an irreversible process - atrophy of the eyeball.
Treatment at home involves the use of eye drops: Trimecaine, Leocaine, Dicaine, Collargol, etc. Products with aloe extract, as well as B vitamins (B1), are useful.
Symptoms indicating the presence of elevated IOP
So, doctors advise paying attention to the following phenomena, which may indicate increased ophthalmotonus. People who already have relatives with glaucoma in their family should be especially attentive to eye health:
- pain in the temples and above the eyebrows when raising the eyes upward, especially in the evening;
- frequent headaches and the inability to get rid of them even with the help of medications;
- burst blood vessels on the white of the eye;
- severe eye fatigue in the evening, discomfort when looking up or to the sides;
- blurred vision after a night's sleep, when it takes time for it to return to normal;
- rapid eye fatigue during visual work;
- decreased clear visibility when moving from a bright room to a darker one.
Here are the main symptoms of so-called eye hypertension, which doctors advise you to pay attention to, especially if you are predisposed to glaucoma. If they recur regularly, then this is a reason to contact a specialist for a thorough examination of the visual organs.
Clinical picture
Most often, eye diseases do not manifest themselves at an early stage. Violations become noticeable when the pathology becomes more serious or already advanced.
Increased intraocular pressure may be a symptom of another disease or occur on its own, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- headache;
- increased fatigue in the eyes;
- feeling of fullness;
- blurred vision;
- rupture of small vessels in the eyeball;
- blurriness of the visible picture.
Only an ophthalmologist can confirm or refute the pathology. Therefore, if you have even one symptom from the list above, you should contact a specialist.
Treatment of high eye pressure
Today, the most common and accessible way to reduce increased ophthalmotonus is the use of special drops that normalize it. But it is also necessary to take into account the reasons that provoked the increase in IOP, and, if possible, eliminate or treat them. In addition to drops, there are also several other methods of combating high eye pressure. An ophthalmologist can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures (vacuum massage, color pulse therapy, etc.), which are carried out in a hospital setting.
The most drastic way to normalize blood pressure is surgery. There are also several types of them: goniotomy, trabeculectomy and the most advanced method - laser surgery. With the help of a laser beam, the outflow pathways of intraocular fluid are opened, as a result of which the ophthalmotonus decreases. But, unfortunately, in order to undergo the operation, the patient must meet certain requirements, and not everyone fits them. In any case, the treatment method is selected individually depending on age, severity of the disease, and individual characteristics of the body.
Prevention of increased intraocular pressure
For minor IOP deviations, a positive result can be obtained by following the following recommendations:
- Enriching the diet with foods rich in omega-3, vitamins A, C and E.
- Buy a high-quality high pillow that provides an elevated position of the head during sleep.
- Do regular eye exercises.
- Wear safety glasses when working on a computer monitor or tablet.
- Correctly organize the workload on the eyes. Take breaks every half hour.
- Avoid excessive participation in strenuous sports.
- Replace caffeinated drinks with herbal infusions with blueberries.
- Do not be nervous. To do this, learn to cope with stressors through relaxation and sports.
Have your vision checked annually by an ophthalmologist. This is especially necessary to do in adulthood. Small changes in intraocular pressure occur unnoticed, but they negatively affect the condition of the visual apparatus. If you want to keep your eyes healthy and your vision clear into old age, don't neglect eye exams.
Normal eye pressure
The ophthalmotonus of an adult normally should not go beyond 10-23 mm Hg. Art. This level of pressure allows you to maintain microcirculatory and metabolic processes in the eyes, and also maintains the normal optical properties of the retina.
Decreased eye pressure is very rare; most eye dysfunction is associated with increased pressure inside the eye. Problems with pressure inside the eye begin more often in patients who have reached the age of forty. If you do not take timely measures to normalize it, you can get glaucoma.
It should be taken into account that IOP (intraocular pressure) may fluctuate throughout the day. For example, in the morning it is higher, and in the evening it gradually decreases. As a rule, the difference in indicators is no more than 3 mm Hg. Art.
Ophthalmotonus is corrected with the help of medications, but for a positive effect the eyes need to get used to them. In addition, medications are selected strictly individually; it happens that a patient tries several types of them, but there is no effect.
Low pressure inside the eyes or ocular hypotension
Reasons for decreased IOP:
- Decreased blood pressure. It has been scientifically proven that arterial and intraocular pressure are closely related. With hypotension, there is a decrease in pressure in the eye capillaries, and as a result, a decrease in IOP.
- Complications after surgery.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the eyeball (iritis, uveitis, etc.)
- A foreign body or eye injury can lower IOP and lead to atrophy of the apple in the eye.
- Dehydration that occurs with severe inflammation and infections (peritonitis, dysentery, cholera).
- Kidney diseases.
- Retinal detachment.
- Underdeveloped eyeball.
Symptoms of ocular hypotension
If the cause of the decrease is dehydration, inflammation or infection, then the pressure decreases sharply, the patient’s eyes stop shining, become dry, and sometimes the eyeballs even sink.
If ophthalmotonus decreases gradually over a long period of time, then, as a rule, there are practically no symptoms. The only thing the patient can notice is that his vision is gradually deteriorating.
Increased intraocular pressure or ocular hypertension
There are three types of increased pressure inside the eye:
- Stable – IOP is constantly above normal. This pressure inside the eyes is the first sign of glaucoma.
- Labile - IOP periodically increases, and then returns to normal values.
- Transient - IOP increases once and is short-term in nature, and then returns to normal.
Read more about retinal disease - retinal angiopathy. Find out how to make a correct diagnosis and effectively prescribe treatment.
Detailed instructions on the correct treatment of an unpleasant eyelid disease - demodicosis.
Reasons for increased IOP
The most common cause of transient elevated eye pressure is hypertension. Also, the pressure in the eyes may increase due to overwork, for example, when working at the computer for a long time. Most often, in parallel with ophthalmotonus, intracranial pressure also increases.
Often the cause of increased IOP can be stress, disruptions in the nervous system, heart failure, kidney disease, Graves' disease, hypothyroidism, rapid menopause, poisoning.
Increased eye pressure of a stable variety occurs primarily in the presence of glaucoma. Glaucoma usually develops in patients forty years of age and older.
Symptoms of high eye pressure:
- Impaired twilight vision.
- Vision deterioration is actively progressing.
- The field of view is significantly reduced.
- The eyes get tired too quickly.
- Redness of the eyes is observed.
- Intense headaches in the suprafrontal arches, eyes and temporal area.
- Midges or rainbow circles flash before your eyes when you look at the light.
- Discomfort when reading, watching TV or working on a computer.
How to reduce pressure in the eyes?
Only significant fluctuations in ophthalmotonus that affect visual acuity require treatment.
To treat high IOP, the doctor usually prescribes tablets and drops for glaucoma and eye pressure. They reduce the production of intraocular fluid, opening additional pathways for its outflow
In this case, it is important to identify the cause of the pathology and direct treatment to eliminate the main problem.
The following medications are popular today to help relieve eye pressure:
- Timolol.
- Xalatan.
- Pilocarpine.
- Travatan.
- Betoptik.
- Fotil.
- Cosopt.
All these drugs should be used under the strict supervision of a doctor, because they can reduce even normal blood pressure. Do not exceed the indicated dosage.
Doctors usually prescribe Omega-3 fatty acids to patients. They maintain the health of the retina and prevent increased pressure. Sometimes the doctor prescribes drugs to treat hypertension, diabetes, as well as diuretics that can draw excess fluid from tissues. A specialist always recommends doing eye exercises or prescribes glasses. You will have to reconsider your daily routine and diet
It is important to limit the time spent in front of the monitor and TV. You can lower eye pressure at home using traditional methods
An infusion of wild pear shoots, nettle and sleep grass is used as an unconventional means of therapy. It is drunk three times a day before meals. Also use an infusion of motherwort in a proportion of 15 g per 250 ml of hot water. The composition is infused for 60 minutes, filtered and drunk 1 tablespoon 3 times a day. An ointment is made from dandelion and honey in a ratio of 1 to 1 and applied to the eyelids.
Treatment with unconventional methods must be agreed upon with the attending physician, because only he knows how to treat pathology in a given case. These methods are effective only at the initial stage of the disease. In case of advanced disease, surgical intervention will be required. With increased IOP, it is necessary to follow preventive measures, namely:
- It is advised to sleep on a high pillow, which should not be very soft.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of alcohol consumed and quit smoking.
- It is recommended to avoid sweet and flour products, potatoes, pasta and cereals. It is worth increasing the amount of black berries in your diet.
- You need to visit an ophthalmologist once every six months.
- It is necessary to walk in the fresh air more often, lead an active lifestyle and get enough sleep.
- You need to do eye exercises every day, and also use special drops that moisturize them.
You should not attribute eye fatigue to a simple lack of sleep, because such a problem can provoke the development of a dangerous pathology and cause blindness. At the first sign of increased eye pressure, you should consult an ophthalmologist. It is much easier to treat it at the initial stage.
Video:
Treatment
For hypotension, conservative therapy with medications is prescribed. The drugs should restore hydrodynamics in the drainage system of the eye, stop inflammation and reduce the risk of hemorrhages into the vitreous cavity.
Eye drops
To increase intraocular pressure, therapy is carried out with the following types of drugs in the form of eye drops:
- Cycloplegic mydriatics. Increasing the size of the pupil facilitates the circulation of intraocular fluid.
- Vasodilators. They improve blood supply to intraocular structures, increase vascular permeability, which causes plasma to escape. As a result, there is an increase in intraocular pressure.
- Antioxidants: Methylethylpyridinol. Remove free radicals and improve metabolism.
- Synthetic glucocorticosteroid drugs. The most commonly prescribed medications are dexamethasone phosphate. The drugs have an anti-inflammatory effect and prevent macular edema.
Folk remedies
Natural products based on medicinal plants are safe for the eyes and saturate the intraocular structures with vitamins and mineral components. Traditional methods of treatment are used only as additional therapy against the background of complex treatment with medications.
There are the following recipes for eye hypotension:
- A decoction of dill seeds. 20 g of the plant product is ground, after which 250 ml of boiling water is poured. Leave the solution for 30 minutes in a warm and dry place. Drink 4-5 times a day, 50 ml.
- Infusion of oak bark. 30 g of the crushed ingredient is placed in a glass jar, then 500 ml of hot water is poured in and left for 2 hours. The resulting infusion is taken once a day on an empty stomach before breakfast.
- Rosehip fruit drink, rich in antioxidants. A handful of fruits are placed in a glass jar, filled with hot water and left to infuse for 3 days in a cool place. Fruit juice is drunk throughout the day.
- A mixture of blueberries and black currants. Both berries are taken in equal proportions and then ground. Every 200 g of mass is mixed with 2 tsp. flower honey. Use 3 tbsp. l. 3-4 times a day.
- Herbal collection. Take the following ingredients in equal proportions: cinnamon powder, buckwheat, ground ginger root, motherwort, lemon balm sprigs, licorice. 2 tbsp. l. mixture of dried components is poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water. Take the medicine after 30 minutes. Drink up to 3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
The duration of therapy with folk remedies continues for 1-2 weeks, depending on the severity of the pathological process.
Useful video
How to treat low blood pressure:
Treatment of high eye pressure
Today, the most common and accessible way to reduce increased ophthalmotonus is the use of special drops that normalize it. But it is also necessary to take into account the reasons that provoked the increase in IOP, and, if possible, eliminate or treat them. In addition to drops, there are also several other methods of combating high eye pressure. An ophthalmologist can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures (vacuum massage, color pulse therapy, etc.), which are carried out in a hospital setting.
The most drastic way to normalize blood pressure is surgery. There are also several types of them: goniotomy, trabeculectomy and the most advanced method - laser surgery. With the help of a laser beam, the outflow pathways of intraocular fluid are opened, as a result of which the ophthalmotonus decreases. But, unfortunately, in order to undergo the operation, the patient must meet certain requirements, and not everyone fits them. In any case, the treatment method is selected individually depending on age, severity of the disease, and individual characteristics of the body.
How to treat intracranial pressure in infants
Remember: treatment of intracranial pressure in children is prescribed by a neurologist only after a special ultrasound examination or tomography; symptoms alone are not enough to take medications. Only after making sure that the diagnosis is correct, children are prescribed Actovegin injections, and older children are given Glycine tablets. They improve the absorption of glucose by brain cells, and also normalize metabolism and have a positive effect on sleep.
Unlawful interference to promote bicycle helmets worn by children. Bicycle helmet compliance and use, a cluster randomized controlled trial among primary school children in deprived areas
Intracranial hypertension leads to high mortality in patients with various encephalocranial pathologies, hence the importance of recognizing and treating this individual as soon as possible. Nursing care and intervention in these situations is critical to maintaining patient stability
Often the cause of ICP is hypoxia (lack of oxygen). In this case, special water procedures and sedatives are prescribed as treatment. This helps improve blood circulation and oxygen saturation of the brain. As a rule, blood pressure decreases after completing a course of such treatment. Otherwise, stronger medications are prescribed.
Intracranial pressure is the result of a dynamic relationship between the skull and its contents. The contents of the brain or merchant consists of the parenchyma itself, the volume of cerebral blood and the volume of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebral perfusion pressure is defined as the difference between mean arterial pressure and intracranial pressure.
This pressure represents the conduction pressure gradient of cerebral blood flow and therefore oxygen and metabolism. The normal brain automatically regenerates its blood flow to maintain a constant flow regardless of blood pressure by changing cerebral vascular resistance.
The specialist must register the child and set a return date for a re-examination. It is often prescribed after undergoing an ophthalmologist, who must conduct an examination of the fundus, and a course of baby massage, which is necessary for the general improvement of the baby’s condition. After all the described procedures, a re-measurement of head circumference, ultrasound and visual examination are carried out. If, as a result of the examination, the doctor removes the diagnosis, your child will be registered for some time with a mandatory examination every six months.
The brain under normal conditions self-regulates blood flow to ensure a constant flow, regardless of blood pressure, by changing cerebral vascular resistance. Intracranial hypertension, intracranial pressure, care
Intracranial hypertension leads to high mortality in brain injury patients with various diseases, so it is very important to recognize and treat this entity as soon as possible. Nursing and nursing care in these situations is critical to maintaining the patient's stable condition
In rare cases, an increase in the volume and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain tissue can be serious and require surgical intervention. The operation is performed under general anesthesia; a certain amount of excess cerebrospinal fluid is removed to normalize the pressure. Postoperative rehabilitation involves taking auxiliary medications and constant monitoring by a doctor.
The contents or compartment consists of the cerebral parenchyma itself, the volume of cerebral blood and the volume of cerebrospinal fluid. This pressure represents the pressure gradient driving cerebral blood flow and therefore oxygen delivery and metabolism. The brain regulates itself during normal blood flow to ensure a constant flow regardless of blood pressure by changing cerebral vascular resistance. Intracranial pressure is defined as a measurement within the cranial cavity that results from the interaction between the continent and the content.
Eye pressure in children
The normal functioning of the retina and the circulation of substances in the eye are largely ensured by the pressure of the fundus of the eye. Deviation from normal indicators indicates congenital or acquired pathologies.
The main symptoms of the disorders are dryness and discomfort in the eyes, head spasms. Reduced or increased intraocular pressure (IOP) leads to the appearance of glaucoma, uveitis or astigmatism.
Eye pressure is treated with medications and folk remedies.
Normal IOP values
In children, IOP levels are the same as in adults. The norm is considered to be a pressure of 10 to 23 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) according to Maklakov.
This pressure ensures normal optical properties and metabolism in the organs of vision. But IOP can also change over the course of one day. In the morning the measurement results are higher than in the evening.
But such deviations should be in the range of 3 mm Hg. Art.
How is it measured?
There are several methods for determining IOP:
- Contact. Measurement with a tonometer: applanation;
- impressionistic;
- contour dynamic.
Before diagnosing IOP, drops of anesthesia are instilled into the patient, and then the measurement is quickly and painlessly taken with a tonometer.
The first method is used by many ophthalmologists. The patient is given eye drops to give local anesthesia. After which all the liquid is forced out of the eye chamber using a tonometer.
For this method, various types of devices are used: Maklakov weight, Scholz tonometer, Goldmann, Icare. The dynamic contour device gives less accurate indicators than the previous ones.
Measurements are carried out quickly and painlessly for humans.
If pressure cannot be measured using instruments due to injuries, then they resort to the palpation method. To do this, close your eyes and lower the pupil down. The doctor presses on the eyelid with two index fingers. If a pulsation is clearly felt when pressing lightly, then the IOP is normal.
This method is extremely effective and does not have negative consequences for the patient.
Reasons for deviations
In children, the indication for changes in IOP is a violation of fluid secretion in the eyes. And also intraocular pressure increases if the baby has farsightedness. This disease can be passed from parents to children.
In schoolchildren, increased eye pressure appears due to fatigue and tension during study. Disorders in infants occur when the eyeball is underdeveloped.
If a child has previously suffered an eye injury or damaged the area near the organs of vision, this also leads to deviations from normal IOP values. Sometimes disturbances indicate a deterioration in the functioning of other organs:
- thyroid gland;
- hearts;
- liver;
- kidney;
- dehydration.
Symptoms of IOP
Parents should contact a pediatric ophthalmologist if their child complains of frequent headaches and discomfort in the eyes.
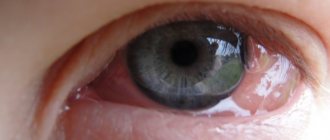
Signs of the disease include noticeable red capillaries in the eyes.
If the normal pressure is violated, the eyes react painfully to light. These are common symptoms of high IOP.
If the pressure is increased, then red capillaries are noticeable in the eyes, nausea and tearfulness appear. Headaches and dry eyes are also signs of hypotension.
If there are violations, the child’s memory and attention deteriorate, and loss of consciousness is possible. Children become lethargic, sleepy and apathetic
Treatment of disorders
At the first signs of the disease, parents should contact an ophthalmologist. You can't ignore the problem, thinking it's just fatigue. Without treatment, abnormal blood pressure leads to vision loss.
Restoration of eye pressure is provided by drops: “Oftolik”, “Vizin”, “Taufon”. They also prescribe medications such as Fotil, Pilocarpine, and Travoprost. All these medications are aimed at restoring fluid circulation in the eyes.
Additionally, doctors advise taking dietary supplements:
- "Blueberry forte";
- "Okuwait Lutein";
- "Super optic."
At home, a tincture of pear root, nettle and sleep herb will help reduce blood pressure. It is recommended to take the decoction 3 times a day.
In addition, brew motherwort (15 grams per 250 ml), let it brew and take 1 teaspoon before meals. It is recommended to wash your eyes with aloe juice 3-4 times a day.
Doctors recommend massaging your eyelids, paying more attention to walks outside and eating right.
Causes of eye hypotony
Intraocular pressure is maintained almost constant, despite the state of health, so it is quite difficult to disturb it. The following conditions can cause eye hypotension:
- retinal detachment (most often a person is predisposed to this from birth, but sometimes it occurs due to injury);
- eye injuries (especially in childhood, when the eyeball has not yet fully formed and is more plastic);
- foreign body entering the eye;
- low blood pressure;
- infectious eye diseases, such as conjunctivitis;
- ireitis, uveitis;
- complications after unsuccessful eye surgery, for example, with laser vision restoration;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- severe dehydration of the body.
Other factors can also lower intraocular pressure: stress, lack of sleep, prolonged contact with a computer, reading in the dark, fatigue, severe weight loss. But the body quickly copes with the consequences of these causes. But the body cannot eliminate the factors listed in the list on its own, so the help of a doctor and therapy are required.
Normal intraocular pressure
2 mm3 of fluid enters the eye every minute. The same amount is allocated from his cells. If this condition is met without violations, then:
- Ophthalmic tone – without deviations;
- The retina works in optimal mode;
- All metabolic processes proceed without deviations.
In general, IOP is considered normal if its value is in the range of 11-21 mmHg. Art. But this indicator is influenced by many factors: for example, the change of season. In summer, according to the observation of ophthalmologists, this figure can decrease by 1 mm Hg. Art., and in winter - to increase the same amount.
The age of a person also plays an important role.
Methods for measuring eye pressure
Intraocular pressure is usually measured during a comprehensive ophthalmologic examination. Palpation is used to roughly determine the IOP level. When the patient looks down with the eyelids closed, low or high pressure can be determined by lightly pressing the upper eyelids with a finger. The differences between the right and left eyes are then compared. Palpation is used when it is not possible to use a measuring device (for example, after corneal transplantation).
Various devices based on different measurement principles are used to measure intraocular pressure. Today, there are 2 main types of tonometers used - contact and non-contact.
Non-contact tonometry
Most often, a patient sees an ophthalmologist using the applanation non-contact method, in which a special air tonometer releases a stream of air to the eye. This pressure flattens the cornea and, according to the measured parameters, determines the IOP values. For the patient, the examination is not burdensome, it is very quick, and is carried out in a sitting position, without contact with the eyes. The method is painless.
Contact tonometry
When using contact applanation tonometers, intraocular pressure is measured by touching the eye (after corneal anesthesia). The device applies pressure to a given area of the cornea necessary to straighten it, directly proportional to the IOP. But measurement results using these types of instruments may not be entirely accurate. They are affected by the shape of the eye, the thickness of the cornea, diseases, and previous surgeries.
Measuring eye pressure through the eyelids
Tonometers that measure IOP through the eyelids are more suitable for screening examinations. Since it is not possible to provide daily intraocular pressure measurements as part of an ophthalmologic examination, devices have been developed to measure IOP even at home. When using this method, there is no direct contact with the eye, no anesthesia is required, and there is no risk of infection. In some serious cases where classical methods cannot be used, transpalpebral tonometry is the best choice.
- corneal edema;
- corneal erosion;
- corneal transplantation.
But the accuracy of these devices is lower compared to other tonometers.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the cause of increased eye pressure and treatment, after establishing an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist. It includes the following activities:
- Palpation. This method is used only if the medical institution does not have special equipment. The doctor presses on the patient's closed eyelids. If the eyeball is dense to the touch, this indicates ocular hypertension.
- Applanation tonometry according to Maklakov. The specialist places weights soaked in paint on the cornea. Then they are transferred to paper and the pressure level is assessed by the diameter of the print.
- Pneumotonometry. This is a non-contact diagnostic method that involves directing a dosed flow of air to the open eye.
- Electrotonography. The doctor installs the sensor from the device on the cornea. The result of the examination is displayed by the computer in graphical form.
Based on the results of the examination and, if necessary, the ophthalmologist can refer the patient for consultation to other specialized specialists.
Symptoms of IOP
A person may not feel symptoms at the initial stage of the disease, which is manifested by heaviness in the eyes and increased fatigue. Such signs are explained by lack of sleep or overwork of the body, but if after rest the symptoms remain, then treatment is necessary. As the disease progresses, it becomes noticeable, causing discomfort to the person. The signs of eye pressure described below will help determine an increase in the indicator:
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- the appearance of bradycardia;
- cloudiness, hazy vision;
- rainbow circles before the eyes;
- severe headaches in the temples or around the eyes;
- dizziness;
- corneal edema;
- lack of pupil reaction to light.
Eye pressure, the symptoms and treatment of which can be suggested by a doctor, is characterized not only by an increase, but also by a decrease in ophthalmotonus. Low reading is less than 10 mm Hg. Art. called ocular hypotony. Symptoms of intraocular pressure due to infection, inflammation and dehydration:
- dryness;
- stop shining;
- sometimes the eyeballs sink;
- gradual deterioration of vision.
Signs of the disease include noticeable red capillaries in the eyes.
If the normal pressure is violated, the eyes react painfully to light. These are common symptoms of high IOP. If the pressure is increased, then red capillaries are noticeable in the eyes, nausea and tearfulness appear. Headaches and dry eyes are also signs of hypotension.
If there are violations, the child’s memory and attention deteriorate, and loss of consciousness is possible. Children become lethargic, sleepy and apathetic
Symptoms and treatment of high type eye pressure are more dangerous to health. As is the case with signs of hypotension, it is difficult to determine and feel the change with increased intraocular pressure. Without a specialist, it will not be possible to identify gradual degenerative changes in the eye that begin with too high pressure.
There are three types of hypertension dynamics:
- stability. High levels remain for a long period without changing - the main sign of the development of glaucoma;
- lability. Iphthalmotonus either jumps or returns to normal;
- transitivity. Hypertension occurs once and then disappears, most often on its own.
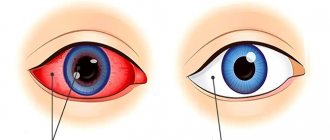
Externally noticeable changes in the eyes with increased intraocular pressure:
- if you look at the photo, you will notice burst blood vessels in people suffering from this condition, and as a result, red eyes;
- tearfulness.
How to identify emerging glaucoma:
- subtle superficial changes in the outer shell of the cornea, which become obvious in the last stages;
- aching, cutting, severe pain in the eyeball;
- vomiting, nausea;
- constant pain in the head, worsening in the temporal and frontal region, around the eyes;
- Red eyes;
- When looking at bright, colored objects, streaks and black spots appear.
Why is it important to pay attention to the signs? This will help return the pressure to normal without consequences, and if glaucoma develops, it will be cured without surgery
Reasons for violation
Ocular hypertension can develop for two reasons:
- Excessive secretion of fluid in the eye chamber.
- Its slow outflow.
Such violations may be episodic or systematic. In the first case, the pathology does not pose a threat to health. It occurs due to the following human conditions:
- physical stress;
- alcohol intoxication;
- cough or vomiting;
- consuming large amounts of caffeinated drinks.
If the disorder is systemic in nature, its etiology usually hides more significant factors:
- anomalies in the structure of the visual apparatus;
- atherosclerosis;
- vascular disorders;
- congenital farsightedness;
- retinal disinsertion;
- damage to eyeball tissue;
- use of certain medications.
If intraocular pressure is persistently elevated, the doctor may diagnose glaucoma. This is a progressive disease that cannot be completely overcome. You can only slow down its progression while maintaining visual function.